Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Water, Solution, Solubility and Hydrogen, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING)
Subject Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Water, Solution, Solubility and Hydrogen, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING)
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: Water, Solution, Solubility and Hydrogen, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Pearson IIT Foundation Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Water, Solution, Solubility and Hydrogen, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING) with Hints & Solutions
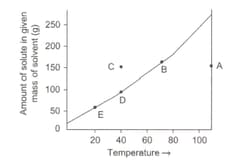
In the above graph, identify the states of solution at the various points A, B, C, D, E. If the solution is cooled from point A, at which temperature precipitation normally starts? Also find out the amount of solute precipitated at and the amount of solute in the solution at point E. What would be the maximum amount of solute that can be precipitated in the process?
A sample of common salt obtained from seawater contains of and of . If it is dissolved in of water and then of water is evaporated, what observation do you find at ? What is the maximum amount of pure that can be obtained by the above method? (solubilities of and are and at and and at respectively).
Explain why temperature in the coastal region is moderate throughout the year.
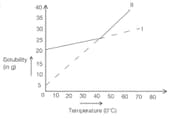
Solubility curves of two salts are shown above. Two processes A and B are carried out in the following ways. In process A, saturated solution of salts I and II at taken at and could slowly to . In process B hot saturated solutions of I and II are cooled from to . Identify the salt precipitated in process A and give reason.
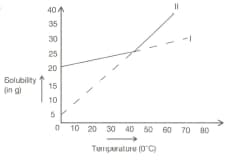
Solubility curves of two salts are shown above. Two processes A and B are carried out in the following ways. In process A, saturated solution of salts I and II at taken at and could slowly to . In process B hot saturated solutions of I and II are cooled from to . Are the precipitated crystals in processes A and B same? Justify your answer.
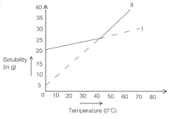
Solubility curves of two salts are shown above. Two processes A and B are carried out in the following ways. In process A, saturated solution of salts I and II at taken at and could slowly to . In process B hot saturated solutions of I and II are cooled from to . of saturated solution of salt I and II is prepared at . Calculate the mass of each salt present in the solution.
A desiccating material is used as a dehumidifying agent for absorbing moisture from highly humid air and again it is made reusable by low humid air. What is the principle involved in this process?
Some of the hydrated crystals are efflorescent. How do you account for this?
