Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 12: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course BITSAT solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
In which of the following figures, the direction of electric field at point is different from others? and represent constant linear charge densities)
A circular ring carries a charge , the variation of electric field with distance measured from centre along axis for is given by Radius of Ring]. The maximum electric field on the axis will be [where ]
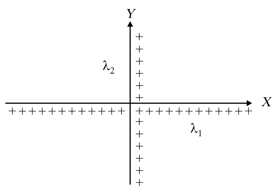
Two non-conducting infinitely long straight wires with uniform linear charge densities and are arranged along and -axis respectively. Their point of intersection is at origin. One of the field lines due to these wires in plane is a straight line passing through the origin. The angle made by this line with -axis is
There is a non-conducting rod of length and negligible mass with two small balls each of mass and electric charge attached to its ends. The rod can rotate in the horizontal plane about a fixed vertical axis crossing it a distance from one of its ends. A uniform horizontal electric field (along axis) is established. At first the rod is in unstable equilibrium. In what position, the rod must be set so that if displaced a little from that position, it begins simple harmonic oscillations about the axis?
There is a non-conducting rod of length and negligible mass with two small balls each of mass and electric charge attached to its ends. The rod can rotate in the horizontal plane about a fixed vertical axis crossing it a distance from one of its ends. A uniform horizontal electric field (along axis) is established. At first the rod is in unstable equilibrium. If it is disturbed slightly from this position, what would be the angular frequency of SHM in the above question?
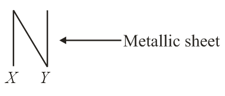
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor when a very thin metallic sheet is placed in the space between the plates, parallel to the plates, will
A thin metallic strip is introduced between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor, touching the plates. How will capacitance change?
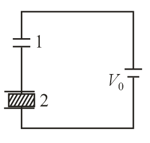
Two identical capacitors and are connected in series. The capacitor contains a dielectric slab of constant as shown. They are connected to a battery of emf volts. The dielectric slab is then removed. Let and be the charge stored in the capacitors before removing the slab and and be the values after removing the slab. Then