B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 6: Exercises
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 6: Exercises
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Elasticity, Exercise 6: Exercises with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced): Mechanics II solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 6: Exercises with Hints & Solutions
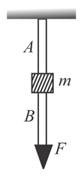
The wires and shown in the figure are made of the same material, and have radii and respectively. The block between them has a mass When the force is one of the wires breaks:
A sphere of radius and mass is attached to the lower end of a steel wire of length and diameter The wire is suspended from high ceiling of a room. When the sphere is made to swing as a simple pendulum, it just grazes the floor at its lowest point. Young's modulus of steel is Find the velocity of the sphere at the lowest position in (Given: )
(Take )
The breaking stress for a metal is The density of the metal is If Find the maximum length of the wire made of this metal which may be suspended without breaking.
The average depth of Indian ocean is about Find the fractional compression of water of the bottom of thc occan. Givcn, bulk modulus of watcr is and density of water
A solid sphere of radius made of a material of bulk modulus is surrounded by a liquid in a cylindrical container. massless piston of area (the area of container is also ) floats un the surface of the liquid. When a mass is placed on the piston to compress the liquid, find the fractional change in radius of the sphere. (Given: )
A wire having a length and cross-sectional area is suspended at one of its ends from a ceiling. Density and Young's modulus of material of the wire are and respectively. Find its strain energy due to its own weight in (Given: )
Find the elastic potential energy per unit volume of water (in ) at a depth of Given, compressibility of water units and density of water
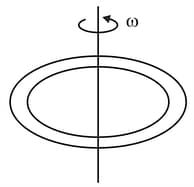
A ring of radius (made of wire of density ) placed on a smooth horizontal surface is rotated about a stationary vertical axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring as shown in figure. Determine the angular velocity in at which the ring breaks. The wire breaks at a tensile stress \sigma. (given and )