B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: System of Particles and Centre of Mass, Exercise 4: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: System of Particles and Centre of Mass, Exercise 4: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 1: System of Particles and Centre of Mass, Exercise 4: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced): Mechanics II solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: System of Particles and Centre of Mass, Exercise 4: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with Hints & Solutions
A small block of mass is projected on a long plank of mass with velocity as shown in figure. Find the work done by friction when slipping stops.
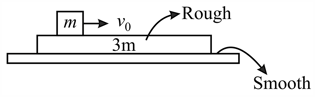
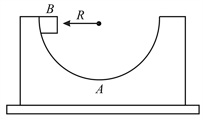
Figure show a block of mass having a smooth semicircular groove of radius placed on a smooth horizontal surface. block of mass is released from a position in groove where its radius is horizontal. Find the speed of bigger block when smaller block reaches its bottommost position.
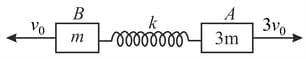
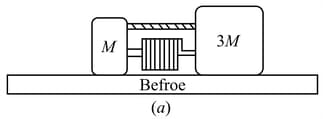
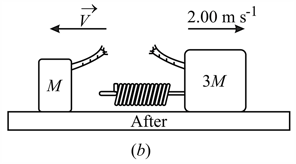
The block of masses and are connected by an ideal spring of force constant Now both the blocks are given impulse in opposite direction so that they started moving with velocities and as shown in the figure. Find the maximum stretch of spring.
In figure a man stands on a boat floating in still water. The mass of the man and the boat is and respectively.
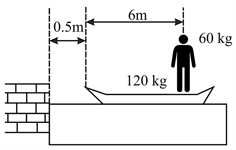
(a) If the man walks to the front of the boat and stops, what is the separation between the boat and the pier now?
(b) If the man moves at a constant speed of relative to the boat, what is the total kinetic energy of the system (boat + man)? Compare this energy with the kinetic energy of the system if the boat was tied to the pier.
An boy and his sister, both wearing roller blades, face each other at rest. The girl pushes the boy hard, sending him backward with velocity towards the west. Ignore friction. (a) Describe the subsequent motion of the girl. (b) How much chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy in the girl's muscles? (c) Is the momentum of the boy-girl system conserved in the pushing apart process? How can it be with no motion beforehand and plenty of motion afterward?
Two blocks of masses and are placed on a horizontal, frictionless surface. A light spring is attached to one of them and the blocks are pushed together with the spring between them. A cord initially holding the blocks together is burned; after that, the block of mass moves to the right with a speed of
(a) What is the velocity of the block of mass
(b) Find the system's original elastic potential energy, taking
(c) Is the original energy in the spring or in the cord? Explain your answer.
(d) Is momentum of the system conserved in the bursting apart process? How can it be with large forces acting? How can it be with no motion beforehand and plenty of motion afterward?
A rifle man, who together with his rifle has a mass of stands on a smooth surface and fires shots horizontally. Each bullet has a mass and a muzzle velocity of
(a) What velocity does the rifle man acquire at the end of shots?
(b) If the shots are fired in what will be the average force exerted on him?
(c) Compare his kinetic energy with that of bullets.
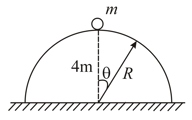
A hemisphere of radius and of mass is free to slide with its base on a smooth horizontal table. A particle of mass is placed on the top of the hemisphere. Find the angular velocity of the particle relative to hemisphere an angular displacement when velocity of hemisphere has become .