K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 6: Exam-style questions
K A Tsokos Physics Solutions for Exercise - K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 6: Exam-style questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 6: Exam-style questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for the IB Diploma 6th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 6: Exam-style questions with Hints & Solutions
A train sounding its horn past a train station without stopping. The train moves at a constant speed. Which is the correct about the frequency of the horn measured by the observer
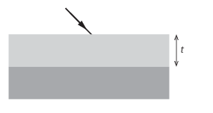
A light is incident essentially normally on a thin film of thickness and refractive index , The film is on a transparent glass of refractive index . Which of the following condition of the wavelength in oil leads to the destructive interference of the reflective light
Light is incident on very thin parallel slits and an interference pattern is formed on a screen a distance away. The number of slits is increased while the separation of two consecutive slits stays the same. Which is correct as N increases?
Monochromatic light of wavelength in air is incident on a rectangular piece of glass of refractive index 1.60 that is coated by a thin layer of magnesium fluoride of refractive index 1.38.

Copy and complete this diagram by drawing the paths of the two rays, originating with the incident ray, that will interfere in the eye of an observer looking down on the glass from above.
State what is meant by the Doppler effect.
Illustrate the Doppler effect for the case of a moving source using wavefront diagrams.
Outline one practical application of Doppler effect.
A disc of radius 0.20 m rotates about its axis making eight revolutions per second. Sound of frequency 2400 Hz is emitted in all directions from a source on the circumference of the disc. The sound is received by an observer far away from the disc. Determine the range of frequencies Hz and the range of wavelengths m that the observer measures.
