Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 2: Exercise#2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 2: Exercise#2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 2: Exercise#2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 2: Exercise#2 with Hints & Solutions
A blackbox which may contain a combination of electrical circuit elements (resistor, capacitor or inductor) is connected with other external circuit elements as shown below in the figure . After the switch is closed at time , the current as a function of time is shown in the figure .
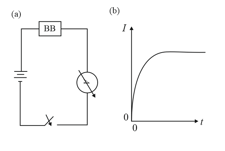
From this we can infer that the blackbox contains
The figure shows a bar magnet and a metallic coil. Consider four situations.
Moving the magnet away from the coil.
Moving the coil towards the magnet.
Rotating the coil about the vertical diameter.
Rotating the coil about its axis.
An emf in the coil will be generated for the following situations.

Two identical metallic square loops and are placed next to each other with their sides parallel on a smooth horizontal table. Loop is fixed and a current which increases as a function of time is passed through it. Then loop :
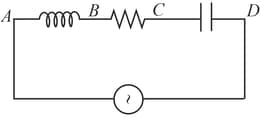
An ac voltmeter connected between points and in the circuit below reads . If it is connected between and , the reading is . The reading when it is connected between and is . What will the voltmeter read when it is connected between and ) Assume that the voltmeter reads true rms voltage values and that the source generated a pure ac.)
A metallic ring of radius a and resistance is held fixed with its axis along a spatially uniform magnetic field whose magnitude is . Neglect gravity. Then
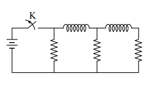
In the circuit shown below, all the inductors (assumed ideal) and resistors are identical. The current through the resistance on the right is after the key has been switched on for a long time. The currents through the three resistors(in order, from left to right) immediately after the key is switched off are:
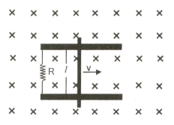
A conducting bar of mass and length moves on two frictionless parallel rails in the presence of a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude directed into the page as shown in the figure. The bar is given an initial velocity towards the right at . Then the
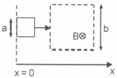
A square-shaped conducting wire loop of dimension a moving parallel to the -axis approaches a square region of size where a uniform magnetic field exists pointing into the plane of the paper (see figure). As the loop passes through this region, the plot correctly depicting its speed as a function of is