Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Nuclear Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise#2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Nuclear Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise#2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 12: Nuclear Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise#2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Nuclear Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise#2 with Hints & Solutions
A radioactive nucleus has a single decay mode with half life . Another radioactive nucleus has two decay modes, and . If decay mode is absent, the half life of would be . If decay mode is absent, the half life of would be . If the actual half life of is , then the ratio is,
A nuclear decay is possible if the mass of the parent nucleus exceeds the total mass of the decay particles. If denotes the mass of a single neutral atom of an element with mass number and atomic number , then the minimal condition that the decay,
will occur is ( denotes the mass of the particle and the neutrino mass can be neglected),
Two species of radioactive atoms are mixed in equal number. The disintegration of the first species is and of the second is . After a long time, the mixture will behave as a species with mean life of approximately,
The half-life of a particle of mass is and a stream of such particles is travelling with the of a particle being . The fraction of particles which will decay when they travel a distance of is,
The binding energy per nucleon of is and that of is . The energy required to remove a neutron from is (mass of electron and proton are and , respectively),
The beta particles of a radioactive metal originate from,
A nuclear fuel rod generates energy at a rate of . It is in the shape of a cylinder of radius and length . A coolant of specific heat flows past it at a rate of . The temperature rise in this coolant is approximately,
The graph shows the log of activity of a radioactive material as a function of time in minutes.
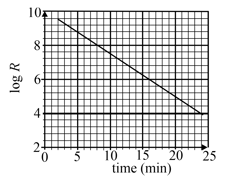
The half-life (in ) for the decay is closest to,
