Maharashtra Board Solutions for Chapter: Heat, Exercise 6: Exercise
Maharashtra Board Science and Technology Solutions for Exercise - Maharashtra Board Solutions for Chapter: Heat, Exercise 6: Exercise
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Heat, Exercise 6: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Science and Technology Standard Ten Part - 1 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Maharashtra Board Solutions for Chapter: Heat, Exercise 6: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
The amount of water vapor in air is determined in terms of its _____. (absolute humidity / absolute temperature)
If objects of equal masses are given equal heat, their final temperature will be different. This is due to difference in their _____ (latent heat / specific heat capacity).
During transformation of liquid phase to solid phase, the latent heat of _____.
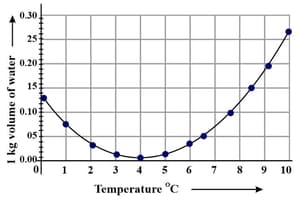
Observe the following graph. Considering the change in volume of water as its temperature is raised from , discuss the difference in the behaviour of water and other substances. What is this behaviour of water called?
Read the following paragraph and answer the question.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both the objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat resistant box (meaning that the energy exchange takes place between the two objects only), then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box.
Heat is transferred from where to where?
Read the following paragraph and answer the question.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both the objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat resistant box (meaning that the energy exchange takes place between the two objects only), then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box.
Which principle do we learn about from this process?
Read the following paragraph and answer the question.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both the objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat resistant box (meaning that the energy exchange takes place between the two objects only), then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box.
How will you state the principle briefly?
Read the following paragraph and answer the question.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both the objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat resistant box (meaning that the energy exchange takes place between the two objects only), then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box.
Which property of the substance is measured using this principle?