Mukesh Kumar Gandhi Solutions for Chapter: Motion in One Dimension, Exercise 2: ILLUSTRATIVE NUMERICALS
Mukesh Kumar Gandhi Physics Solutions for Exercise - Mukesh Kumar Gandhi Solutions for Chapter: Motion in One Dimension, Exercise 2: ILLUSTRATIVE NUMERICALS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Motion in One Dimension, Exercise 2: ILLUSTRATIVE NUMERICALS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Together With Physics Class 9 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Mukesh Kumar Gandhi Solutions for Chapter: Motion in One Dimension, Exercise 2: ILLUSTRATIVE NUMERICALS with Hints & Solutions
A particle moves due east and then through due north. The net distance moved is _____ meter.
A particle moves to east and then through to north. Now, the net displacement is . Find the value of .
A body starts from rest and acquires a velocity in . Find acceleration of the body in
A car moves in and the next in , calculate the average speed for the entire trip in kilometer per hour.
Choose the correct answer from the given options .
A vehicle is accelerating on a straight road. Its velocity at any instant is . After , it is and after further it is . Find the acceleration of the vehicle in SI unit. Is the acceleration uniform?
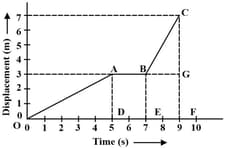
In the given figure, the displacement of an object is shown at different times. Calculate the velocity of the object as it moves from to , to , and .
A car travels with a uniform velocity of for . The brakes are then applied and the car comes to rest with a uniform retardation in a further . Draw a velocity-time graph and use it to find the distance with which the car travels after the brakes are applied.
A car travels with a uniform velocity of for . The brakes are then applied and the car comes to rest with a uniform retardation in a further . Draw a velocity-time graph and use it to find the distance travelled in first , total distance travelled, acceleration during the first and in last .
