A Hall probe is designed to operate with a steady current of in a semiconductor slice of thickness . The number density of charge carriers (electrons) in the semiconductor is .
(b) Explain why the current in the Hall probe must be maintained at a constant value.

Important Questions on Motion of Charged Particles
A scientist is doing an experiment on a beam of electrons travelling at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of flux density . The graph shows the variation of the magnetic force acting on an electron with the speed v of the electron.
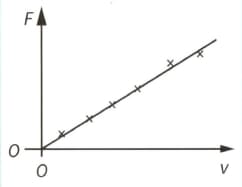
The gradient of the graph is . The magnitude of the charge on the electron is e. What is the correct relationship for the magnetic flux density ?
A , B , C , D
An electron beam is produced from an electron gun in which each electron is accelerated through a potential difference () of When these electrons pass at right angles through a magnetic field of flux density , the radius of curvature of the electron beam is
Calculate the ratio (known as the specific charge of the electron).
Two particles, an -particle and a -particle, are travelling through a uniform magnetic field. They have the same speed and their velocities are at right angles to the field. Determine the ratio of:
(a) the mass of the -particle to the mass of the -particle.
Mass of proton
Two particles, an particle and a particle, are travelling through a uniform magnetic field. They have the same speed and their velocities are at right angles to the field. Determine the ratio of:
(b) the charge of the particle to the charge of theparticle.
Two particles, an -particle and a -particle, are travelling through a uniform magnetic field. They have the same speed and their velocities are at right angles to the field. Determine the ratio of:
(c) the force on the -particle to the force on the -particle
