A ball of mass 0.1 kg strikes a wall normally with a speed of 30 and rebounds with a speed of 20 . The impulse of the force exerted by the wall on the ball is
Important Questions on Laws of Motion
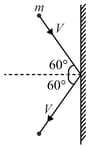
A rigid ball of mass, strikes a rigid wall at and gets reflected without any loss of speed as shown in the figure below. The value of impulse imparted by the wall on the ball will be
(i) second, (ii) seconds, respectively.
Choose the correct option out of the following :
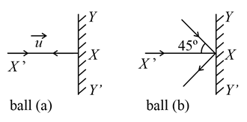
Two billiard balls of equal mass strike a rigid wall with same speed of (as shown) but at different angles. If the balls get reflected with the same speed, then the ratio of the magnitude of impulses imparted to ball and ball by the wall along direction is:
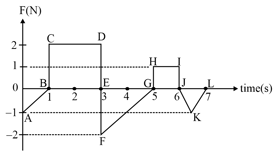
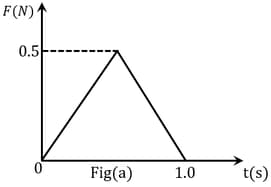
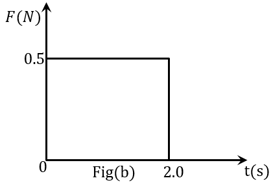
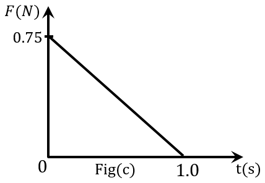
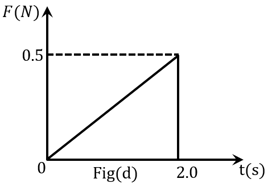
Figures (a), (b), (c) and (d) show variation of force with time.
The impulse is highest in figure.
A ball of mass , moving with a speed of , strikes a wall at an angle (as shown in figure). The ball rebounds at the same speed and remains in contact with the wall for ; the force exerted by the ball on the wall is:
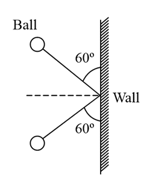
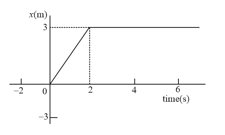
Figure represents the position-time graph of a body of mass . Impulse imparted to the body at is
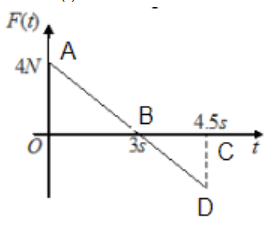
The force acting on a particle of mass is indicated by the force-time graph shown below. The change in momentum of the particle over the time interval from zero to is:
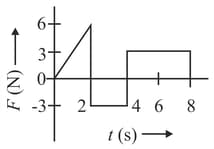
A force-time graph for a linear motion of a body is shown in the figure. The change in linear momentum between and is