A circular disk of moment of inertia is rotating in a horizontal plane, about its symmetry axis, with a constant angular speed . Another disk of moment of inertia is dropped coaxially onto the rotating disk. Initially the second disk has zero angular speed. Eventually both the disks rotate with a constant angular speed .The energy lost by the initially rotating disk to friction is:

Important Questions on Rotational Mechanics
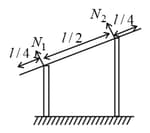
A uniform rod of length is placed symmetrically on two walls as shown in figure. The rod is in equilibrium. If and are the normal forces exerted by the walls on the rod, then,
STATEMENT 1: The total translational kinetic energy of all the molecules of a given mass of an ideal gas is times the product of its pressure and its volume. Because
STATEMENT 2: The molecules of gas collide with each other and the velocities of the molecules change due to the collision.
Assertion: If two different axes are at same distance from centre of mass of a rigid body, then moment of inertia of the given rigid body about both axes will always be same.
Reason: A thin uniform rod is undergoing fixed axis rotation about one of its ends with variable angular acceleration. Then, the acceleration vector of any two moving points on the rod cannot be parallel at an instant of time.
Assertion: A rigid disc rolls without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface with uniform angular velocity. Then, the acceleration of lowest point on the disc is zero.
Reason: For a rigid disc rolling without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface, the velocity of the lowest point on the disc may be non-zero.
Assertion : If the momentum of a particle is constant, then its angular momentum will also be constant
Reason : When net external force on an object is zero, then external torque on the object will also be zero.
Reason : In the situation of statement-1, the centres of both spheres have the same acceleration and they travel the same distance. Hence time taken is same.
Assertion: A thin uniform rod is undergoing fixed axis rotation about one of its ends with variable angular acceleration. The acceleration vector of any two moving points on the rod can not be parallel at any instant of time.
Reason: For a rod undergoing fixed axis rotation, the velocity of any two moving points on the rod at different distances from the centre of rotation is different.
Assertion: A rigid disc rolls without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface with uniform angular velocity. Then the acceleration of the lowest point on the disc is zero.
Reason: For a rigid disc rolling without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface, the velocity of the lowest point on the disc is always zero.
