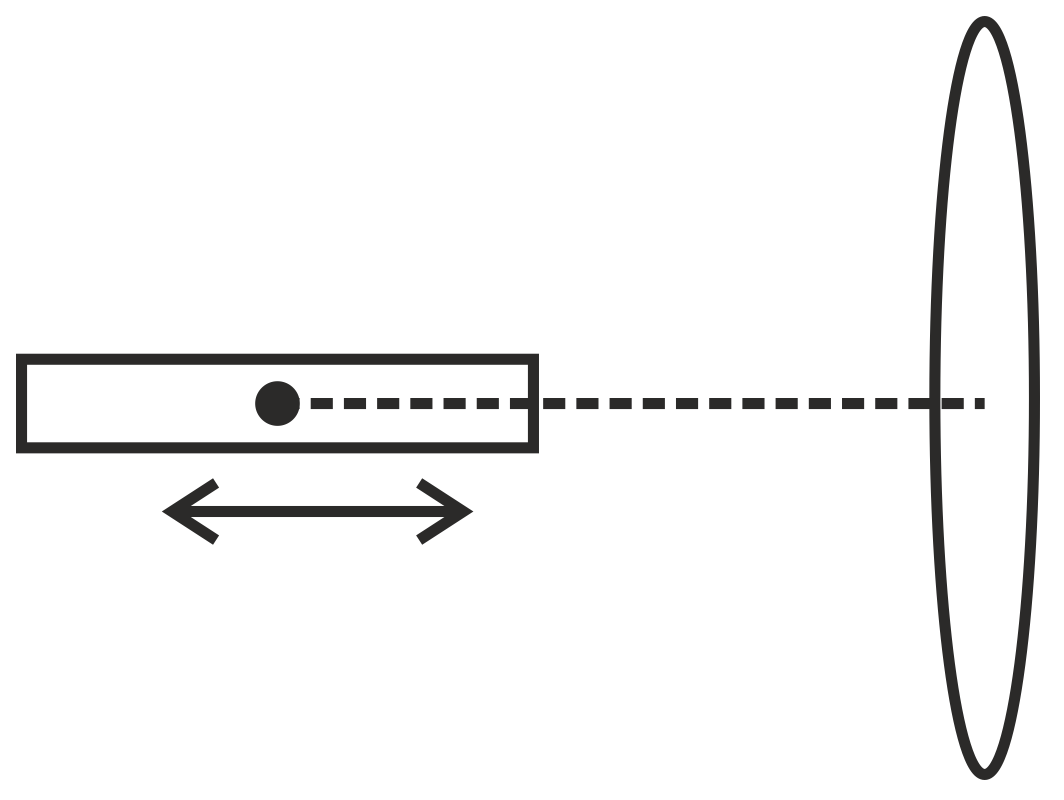
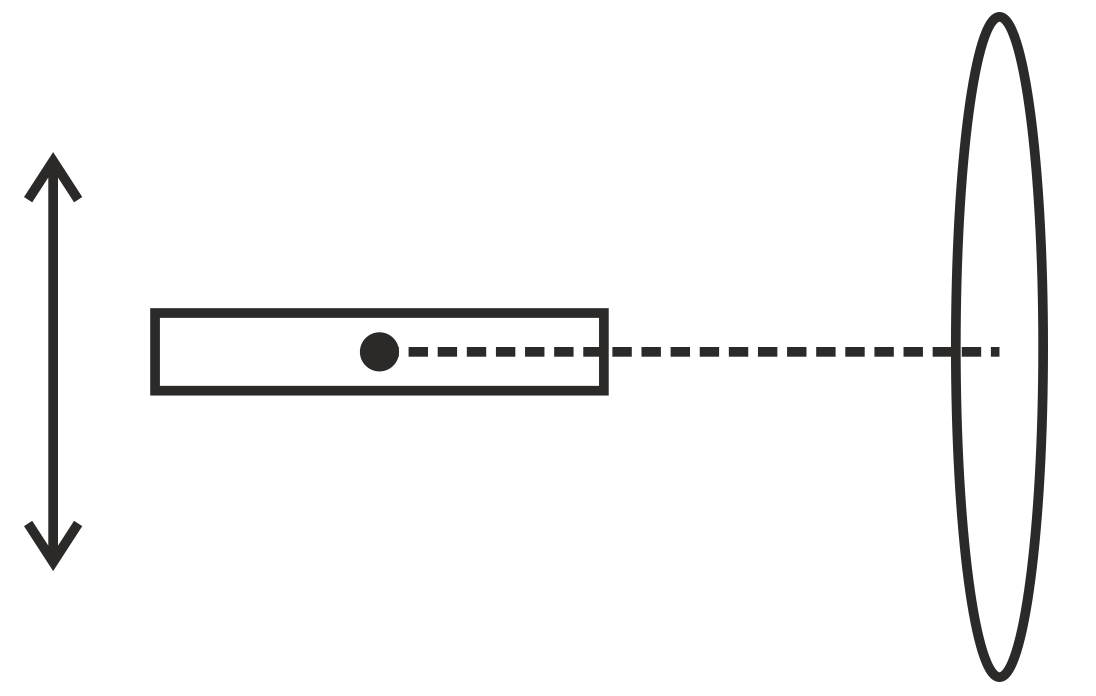
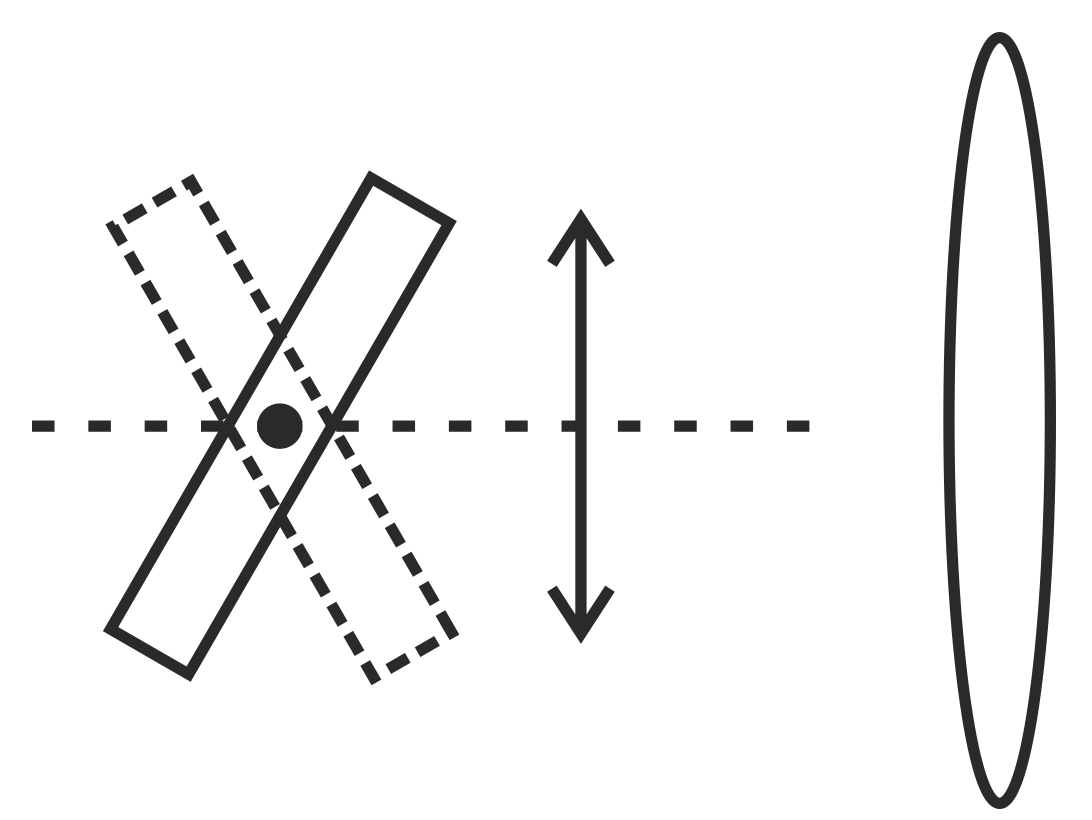
A magnetic bar is in front of a coil as shown below. The line joining the center of the bar and the center of the coil (central axis) is perpendicular to the plane of the coil. Which of the following motions of the bar will NOT induce electric current in the coil?
Translational motion back and forth
Translational motion up and down.
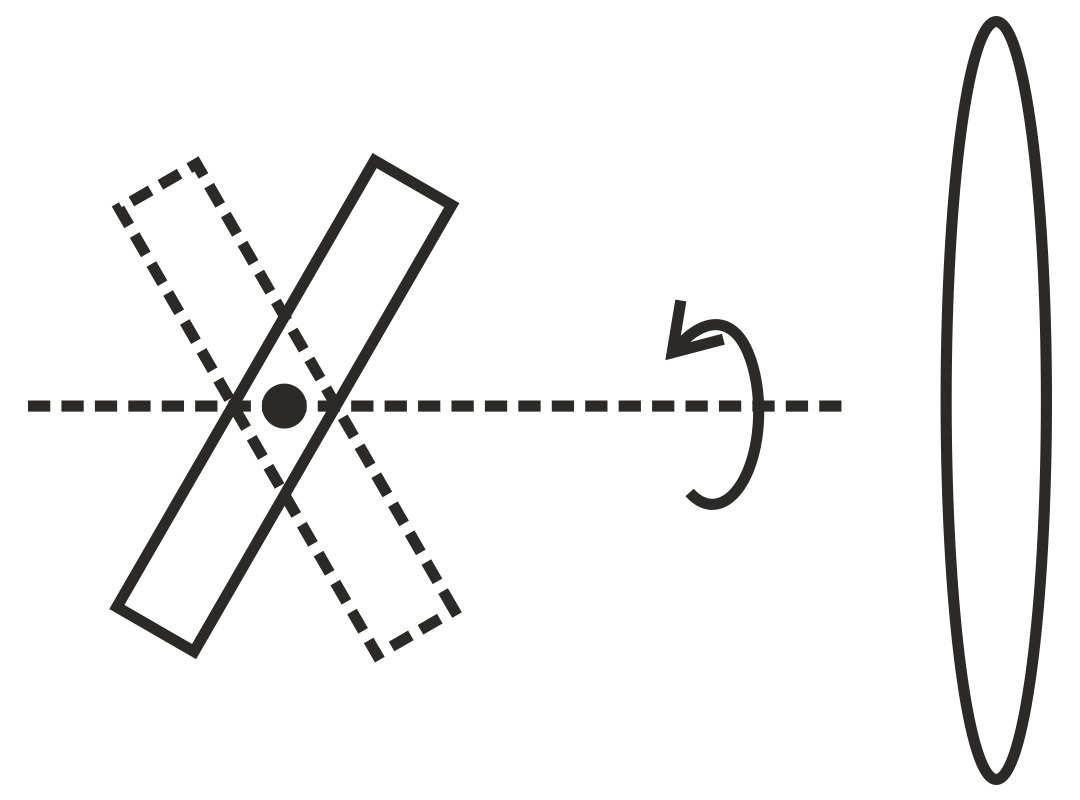
The bar axis swings back and forth about the central axis within the paper plane.

Important Questions on Electromagnetic Induction
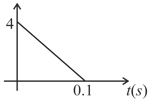
When magnetic flux through a coil is changed, the variation of induced current in the coil with time is as shown in graph. If resistance of coil is , then the total change in flux of coil will be-
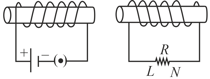
Two co-axial solenoids shown in figure. If key of primary suddenly opened then direction of instantaneous induced current in resistance ' ' which connected in secondary :-
As a result of change in the magnetic flux linked to the closed loop shown in the figure, an e.m.f. . volt is induced in the loop. The work done (joules) in taking a charge coulomb once along the loop is :-
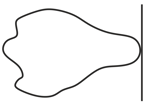
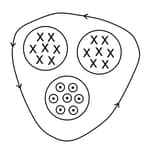
Figure shows three regions of magnetic field each of area and in each region magnitude of magnetic field decreases at a constant rate . If is induced electric field, then value of line integral along the given loop is equal to,
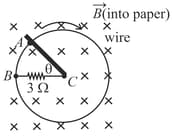
The drawing shows a copper wire (of negligible resistance) bent into a circular shape with a radius of . The radial section is fixed in plane, while the copper bar sweeps around at an angular speed of . The bar makes electrical contact with the wire at all times. The wire and the bar have negligible resistance. uniform magnetic field exists everywhere, is perpendicular to the plane of the circle, and has a magnitude of . Which of the following shows the magnitude of the current as a function of ?
As shown, a uniform magnetic field pointing out of the paper plane is confined in the shaded area of radius . At a distance from the centre of the shaded area there is a point particle of mass and carrying charge . The magnetic field is then quickly changed to zero. Find the speed of the particle.