A small steel ball falls through a syrup at constant speed of . If the steel ball is pulled upwards with a force equal to twice its effective weight, how fast will it move upwards?

Important Questions on Viscosity and Surface Tension
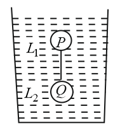
Two spheres and of equal radii have densities and , respectively. The spheres are connected by a massless string and placed in liquids and of densities and viscosities and , respectively. They float in equilibrium with the sphere in and sphere in and the string is being taut (see figure). If sphere alone in has terminal velocity and alone in has terminal velocity , then
where coefficient of viscosity, so dimensions of will be :
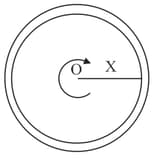
The diagram shows a cup of tea seen from above. The tea has been stirred and is now rotating without turbulence. A graph showing the speed with which the liquid is crossing points at a distance from along a radius would look like
The radii of the two columns in a -tube are and . When a liquid of density '' (angle of contact is ) is filled in it, the level difference of the liquid in the two arms is ''. The surface tension of the liquid is :
( - accelaration due to gravity)
If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is
