A time dependent force acts on a particle of mass . If the particle starts from rest, the work done by the force during the first will be:

Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
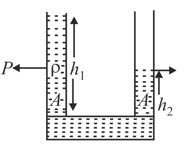
Two identical cylindrical vessels with their bases at the same level each contain a liquid of density as shown in the figure. The height of the liquid in one vessel is and in other vessels , the area of either base is . Find the work done by gravity in equalizing the levels when the two vessels are connected.
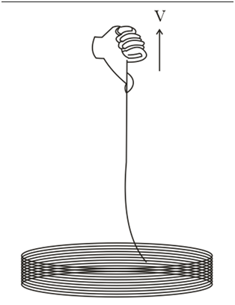
A uniform rope of linear mass density and length is coiled on a smooth horizontal surface. One end is pulled up with constant velocity Then find average power applied by the external agent in pulling the entire rope just off the ground ?
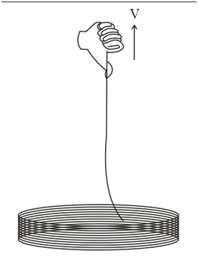
A uniform rope of linear mass density and length is coiled on a smooth horizontal surface. One end is pulled up with a constant velocity . The maximum power delivered by the agent in pulling up the rope is?
Two blocks of mass respectively are joined to the ends of an undeformed massless spring of spring constant . They can move on a horizontal smooth surface. Initially have velocities towards left and towards right respectively. Constant forces of magnitudes are always acting on respectively in the directions shown. Find the maximum extension in the spring during the motion.
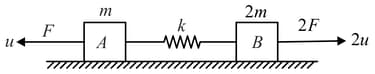
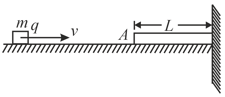
Figure shows a rod of length which is uniformly charged with linear charge density kept on a smooth horizontal surface. Right end of rod is in contact with a vertical fixed wall. A block of mass m and charge q is projected with a velocity from a point very far from rod in the line of rod. Find the distance of the closest approach between the block & the left end of the rod.
A non-conducting disc of radius and uniform positive surface charge density is placed on the ground with its axis vertical. A particle of mass and positive charge is dropped along the axis of the disc from a height with zero initial velocity. The particle has, .
(i) Find the value of if the particle just reaches the disc.
(ii) Sketch the potential energy of the particle as a function of its height and find its equilibrium position.
