EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
An ideal gas is allowed to expand both reversibly and irreversibly in an isolated system. If is the initial temperature and is the final temperature, which of the following statements is correct?
(a)
(b) for both reversible and irreversible processes
(c)
(d) for reversible process but for irreversible process
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A Carnot engine works between constant temperature and of source and sink, respectively. For efficiency to be greatest
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Two carnot engines and are operated in series. The first one, receives heat at and rejects to a reservoir at temperature The second engine receives heat rejected by the first engine and, in turn, rejects to a heat reservoir at Calculate the temperature if the work outputs of the two engines are equal:
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A reversible engine converts one-sixth of the heat input into work. When the temperature of the sink is reduced by , the efficiency of the engine is doubled. The temperatures of the source and sink are
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A Carnot engine takes 300 calories of heat from a source at and rejects calories of heat to the sink. The temperature of the sink is
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
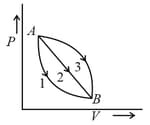
A given mass of a gas expands from state to by three different paths , and as shown in the diagram. If , and respectively be the work done by the gas along three paths, then
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Two carnot engine are connected in series and output work of both engine is same. If temperature of source of engine is and temperature of sink of engine is The temperature of junction will be
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A certain engine which operates in a carnot cycle absorbs at , how much work is done by the engine per cycle? The temperature of sink is .
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A carnot engine working between and has work output of . What is the amount of heat energy supplied to the engine from source per cycle
