HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spring loaded piston (as shown in the figure). Initially the gas is at temperature , pressure and volume and the spring is in its relaxed state. The gas is then heated very slowly to temperature , pressure and volume . During this process the piston moves out by a distance . Ignoring the friction between the piston the cylinder, the correct statement(s) is (are)
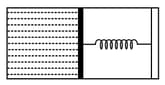
(a)If and , then the energy stored in the spring is
(b)If and , then the change in internal energy is
(c)If and , then the work done by the gas is
(d)If and , then the heat supplied to the gas is
28.57% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
Consider one mole of helium gas enclosed in a container at initial pressure and volume . It expands isothermally to volume . After this, the gas expands adiabatically and its volume becomes . The work done by the gas during isothermal and adiabatic expansion processes are and , then is _________ .
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
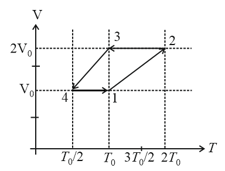
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas goes through a thermodynamic cycle, as shown in the volume versus temperature diagram. The correct statement(s) is/are:
[ is the gas constant]
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
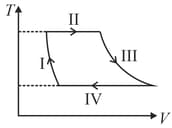
One mole of a monatomic ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process as shown in the figure (where V is the volume and T is the temperature). Which of the statements below is (are) true?
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
An ideal gas is undergoing a cyclic thermodynamic process in different ways as shown in the corresponding P-V diagrams in column 3 of the table. Consider only the path from state to state . denotes the corresponding work done on the system. The equations and plots in the table have standard notations as used in thermodynamic process. Here is the ratio of heat capacities at constant pressure and constant volume. The number of moles in the gas is .
| Column – 1 | Column – 2 | Column – 3 |
| (I) | (i) Isothermal | (P) 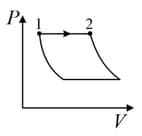 |
| (II) | (ii) Isochoric | (Q) 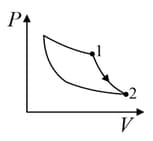 |
| (III) | (iii) Isobaric | (R) 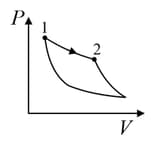 |
| (IV) | (iv) Adiabatic | (S) 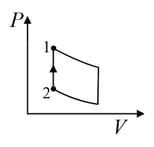 |
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
An ideal gas is undergoing a cyclic thermodynamic process in different ways as shown in the corresponding P-V diagrams in column 3 of the table. Consider only the path from state 1 to state 2. W denotes the corresponding work done on the system. The equations and plots in the table have standard notations as used in thermodynamic process. Here is the ratio of heat capacities at constant pressure and constant volume. The number of moles in the gas is .
| Column – 1 | Column – 2 | Column – 3 |
| (I) | (i) Isothermal | (P) 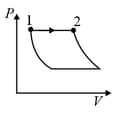 |
| (II) | (ii) Isochoric | (Q) 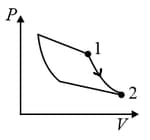 |
| (III) | (iii) Isobaric | (R) 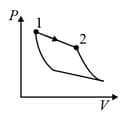 |
| (IV) | (iv) Adiabatic | (S) 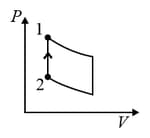 |
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
An ideal gas is undergoing a cyclic thermodynamic process in different ways as shown in the corresponding P-V diagrams in column 3 of the table. Consider only the path from state 1 to state 2. W denotes the corresponding work done on the system. The equations and plots in the table have standard notations as used in thermodynamic process. Here is the ratio of heat capacities at constant pressure and constant volume. The number of moles in the gas is n.
| Column – 1 | Column – 2 | Column – 3 |
| (I) | (i) Isothermal | (P) 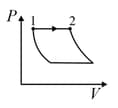 |
| (II) | (ii) Isochoric | (Q) 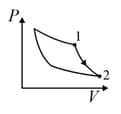 |
| (III) | (iii) Isobaric | (R) 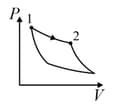 |
| (IV) | (iv) Adiabatic | (S) 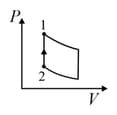 |
