An infinite non-conducting sheet with a uniform surface charge density sets up parallel equipotential surfaces. Any pair of surfaces differing by are separated by . What is the magnitude of the surface charge density? If an electron is released near the sheet, does it tend to move from higher to lower potential or vice versa?

Important Questions on Electric Potential
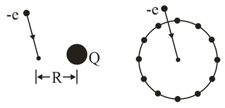
In figure , we move an electron from an infinite distance to a point at distance from a tiny charged ball. The move requires work by us. What is the charge on the ball? In figure , the ball has been sliced up and the slices spread out so that an equal amount of charge is at the hour positions, on a circular clock face of radius . Now the electron is brought from an infinite distance to the centre of the circle. With that addition of the electron to the system of charged particles, what is the change in the electric potential energy of the system?
Two isolated, concentric conducting spherical shells have radii and uniform charges and , and negligible thicknesses. What is the magnitude of the electric field at radial distance , and ? With at infinity, what is at , , , , and ? Sketch and .
Two metal spheres, each of radius , have a centre-to-centre separation of . Sphere has charge and sphere has charge . Assume that the separation is large enough for us to say that the charge on each sphere is uniformly distributed (the spheres do not affect each other). With at infinity, calculate the potential at the point halfway between the centres and the potential on the surface of sphere and sphere .
