Cloud formation condition
Consider a simplified model of cloud formation. Hot air in contact with the earth’s surface contains water vapour. This air rises connectively till the water vapour content reaches its saturation pressure. When this happens, the water vapour starts condensing and droplets are formed. We shall estimate the height at which this happens. We assume that the atmosphere consists of the diatomic gases oxygen and nitrogen in the mass proportion respectively. We further assume that the atmosphere is an ideal gas, the acceleration due to gravity is constant and air processes are adiabatic. Under these assumptions one can show that the pressure is given by
Here and is the pressure and temperature respectively at sea level is the lapse rate (magnitude of the change in temperature with height above the earth’s surface, i.e. ).
(a) Obtain an expression for the lapse rate in terms of and . Here is the ratio of specific heat at constant pressure to specific heat at constant volume; , the gas constant; and , the relevant molar mass.
(b) Estimate the change in temperature when we ascend a height of one kilometre ?
(c) Show that pressure will depend on height as given by Eq. (1). Find an explicit expression for exponent in terms of .
(d) According to this model what is the height to which the atmosphere extends? Take and

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
A paddle wheel is connected with a block of mass as shown in the figure. The wheel is completely immersed in the liquid of heat capacity . The container is adiabatic. For the time interval in which block goes down slowly calculate
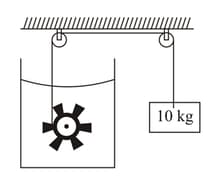
Work done on the liquid
Heat supplied to the liquid
The rise in the temperature of the liquid
Neglect the heat capacity of the container and the paddle.
Find the work done by gas going through a cyclic process shown in the figure?
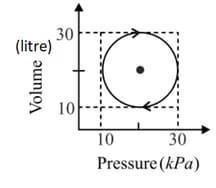
Find the work done by an ideal gas during a closed cycle shown in the figure if and segments and of the cycle are parallel to the -axis?
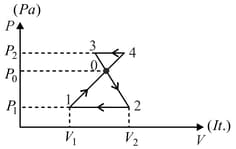
In given figure, when a thermodynamic system is taken from state to state via path , of heat given to the system and work is done by the gas. Along the path , the work done by the gas is Find the heat flowing into the system in this case?