EASY
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Density of a solution of acetic acid in water is . Determine the molality(mol/kg) of the solution.
Round of the answer up to two places of decimal.
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Solution & Colligative Properties
MEDIUM
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
A mixture of ethyl alcohol and propyl alcohol has a vapour pressure of at . The vapour pressure of propyl alcohol is . Determine the vapour pressure of ethyl alcohol is , its vapour pressure (in ) at the same temperature would be:
EASY
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
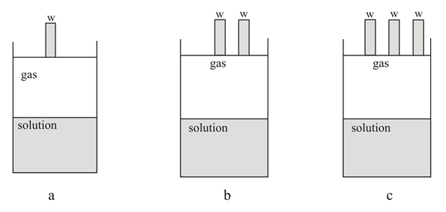
The solubility of a gas in a solution is measured in three cases as shown in the figure given below, where is the weight of a solid slab placed on the top of the cylinder lid. The solubility will follow the order:
MEDIUM
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
The boiling points of aqueous solutions of sucrose, and would be:
MEDIUM
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
A dilute aqueous solution of a polymer of known molecular weight shows an elevation of boiling point of water by . The molar boiling point elevation constant of water is . Using these data-
HARD
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
The freezing point of pure benzene is . When of butane is dissolved in of benzene, the freezing point of benzene decreases to . To lower the freezing point of benzene by another , the amount of butane that has to be added to mixture is:
MEDIUM
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
The addition of of a compound to of benzene (density ) lowers the freezing point from to . If the freezing point constant, , for benzene is , the molar mass of the compound is approximately:
MEDIUM
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
A solution containing of nicotine in of water freezes degrees below the normal freezing point of water. If the molal freezing point depression constant, , then the molar mass of nicotine is:
EASY
KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX
IMPORTANT
At , the ratio of osmotic pressures of two solutions of a substance with concentrations of and , respectively, is:
