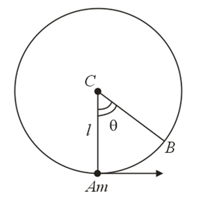
For a particle in uniform circular motion, the acceleration at a point on the circle of radius is (here is measured from the -axis)

Important Questions on Circular Motion
A particle of mass is attached at one end of a light, an inextensible string of length whose other end is fixed at the point . At the lowest point, the particle is given minimum velocity to complete the circular path in the vertical plane. As it moves in the circular path the tension in the string changes with is defined in the figure. As varies from (i.e. the particle completes one revolution) plot the variation of tension against .
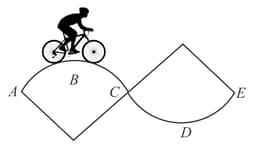
A track consists of two circular parts and of equal radius and joined smoothly as shown in the figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing together with the rider travels at a constant speed of on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at and . (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at and . (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just, before and just after the cycle crosses . (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take .
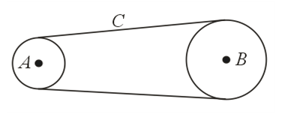
A wheel of radius, is coupled by a belt to another wheel of radius, as in the figure. The belt does not slip. At time , wheel increases its angular speed from rest at a uniform rate of . Find the time in which wheel attains a speed of (wheel are fixed).
A rod is moving on a fixed circle of radius with constant velocity as shown in the figure. is the point of intersection of the rod and the circle. At an instant, the rod is at a distance from centre of the circle. The velocity of the rod is perpendicular to the rod and the rod is always parallel to the diameter .
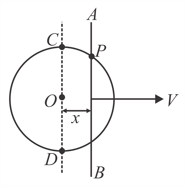
(a) Find the speed of the point of intersection .
(b) Find the angular speed of the point of intersection with respect to centre of the circle.
A small sphere of mass suspended by a thread is first taken aside so that the thread forms the right angle with the vertical and then released, then:
(i) Find the total acceleration of the sphere and the thread tension as a function of , (the angle of deflection of the thread from the vertical).
(ii) Find the angle between the thread and the vertical at the moment when the total acceleration vector of the sphere is directed horizontally.
(iii) Find the thread tension at the moment when the vertical component of the sphere’s velocity is maximum.
