For each of the materials whose stress-strain graphs are shown in Figure, deduce the values of the Young modulus.
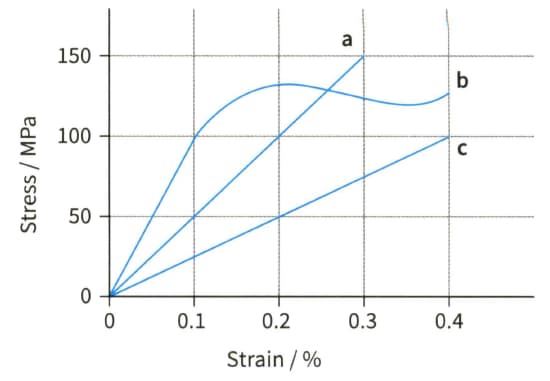
Stress-strain graphs for three materials.


Important Questions on Matter and Materials
Figure shows force-extension graphs for two materials. For each of the following questions, make the statement required. Also explain how you deduce your answer from the graphs.
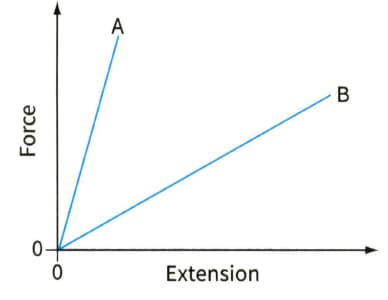
Force-extension graph for two polymers.
(a) State which polymer has the greater stiffness.
Figure shows force-extension graphs for two materials. For each of the following questions, make the statement required. Also explain how you deduce your answer from the graphs.
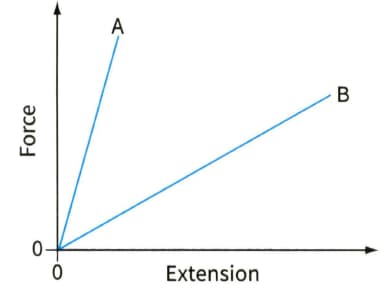
Force-extension graph for two polymers.
(b) State which polymer requires the greater force to break it.
Figure shows force-extension graphs for two materials. For each of the following questions, make the statement required. Also explain how you deduce your answer from the graphs.
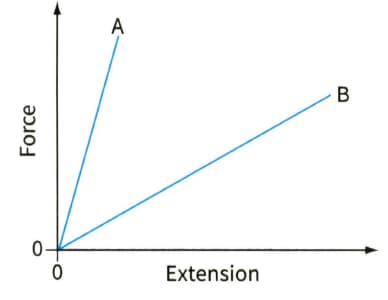
Force-extension graph for two polymers.
(c) State which polymer requires the greater amount of work to be done in order to break it.
Which force is caused by a difference in pressure?
(A) Drag
(B) Friction
(C) Upthrust
(D) Weight
Two wires and both obey Hooke's law. They are both stretched and have the same strain. The Young modulus of is four times larger than that of . The diameter of is twice that of . What is the ratio of the tension in to the tension in ?
(A)
(B) 0
(C)
(D)
