In a chemical reaction, enzymes catalyze the reaction by:
Important Questions on Biomolecules
Study the following
| (I) | value | Affinity of the enzyme | Inverse measure enzyme affinity |
| (II) | Hydrolases | bonds | Linking compounds |
| (III) | Transferases | Transfer of a group | Inhibitor of reaction |
| (IV) | Emil Fisher | Lock and key hypothesis | Formation of ES complex |
The correct combinations are
The graph below depicts the velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction vs. substrate concentration. Identify the alphabets with the correct descriptions.
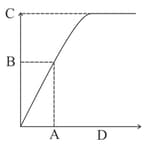
I. Enzyme activity
II. Substrate concentration at maximum velocity
III. Substrate concentration at which half of the maximum velocity
IV. Half of the maximum velocity
Find out where transketolase and epimerase reactions occur among the following:
i) Fructose bisphosphate
ii) Sedoheptulose- Phosphate Xylulose Ribose Phosphate
iii) Ribose Phosphate Ribulose Phosphate
iv) Xylulose Phosphate Ribulose Phosphate
v) Fructose Phosphate XylulosePhosphate Erythrose Phosphate
The correct combination is
The following graph shows the concentration of substrate on enzyme activity:
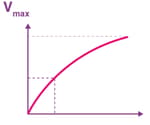
What does the -axis represent?
Coenzyme or metal ion that is tightly bound to enzyme protein is called prosthetic group.
A complete catalytic active enzyme with its bound prosthetic group is called apoenzyme.
Select the correct option.
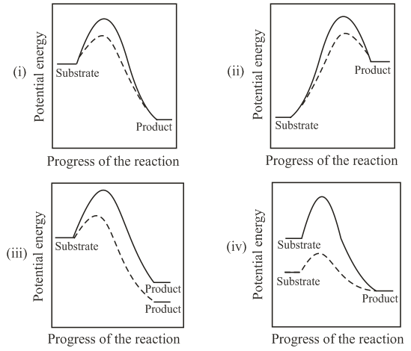
The following graphs with the solid and dotted lines correspond to the reactions without and with enzyme, respectively. Which of the following graph(s) correctly represents the concept of activation energy?
Match the enzymes in Column I with their respective biochemical reactions in column II. Choose the correct combination from below
| Column I | Column II |
| (P) Transaminases | (i) Removal of a phosphoryl group from a specific amino acid |
| (Q) Protein Kinases | (ii) Removal of α-amino group from a specific amino acid |
| (R) Protein Phosphatases | (iii) Addition of phosphoryl group to a specific amino acid |
| (S) Dehydrogenases | (iv) Interconversion of optical isomers |
| (v) Oxidation and reduction of substrates |