Enzymes
Enzymes: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Ribozyme, Energy Profile of Enzyme Action, Enzymes, Nomenclature of Enzymes, Oxidoreductase, Transferase, Hydrolases, Lyases, Isomerases, Ligases, Enzyme Structure, Simple Enzymes, Conjugated Enzymes, etc.
Important Questions on Enzymes
Study the given data and answer the following question.
A sample of an enzyme called lactase was isolated from the intestinal lining of a calf. Assays were undertaken to evaluate the activity of the enzyme sample. The substrate of lactase is the disaccharide lactose. Lactase breaks a lactose molecule in two, producing a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule.
Two assays were carried out.
Assay 1:
| Lactose concentration (% w/v) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Concentration of enzyme sample (% v/v) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| Reaction rate glucose sec-1 mL-1 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 |
Assay 2:
| Lactose concentration (% w/v) | 0 | 5 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Concentration of enzyme sample (% v/v) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Reaction rate glucose sec-1 mL-1 | 0 | 15 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 40 |
Which of the following statements can be concluded from the two assays?
A scientist performed enzyme kinetics and obtained velocity as a function of substrate concentration and the values are given in the table below.
The of the substrate could
The graph given below shows the Michaelis-Menten kinetics for two reactions ( and ; represented as solid and dotted lines, respectively). Enzymes and have values, and , respectively. The respective values for and are and . ().
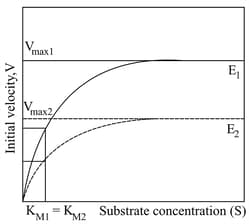
The correct statement(s) for reactions and is/are
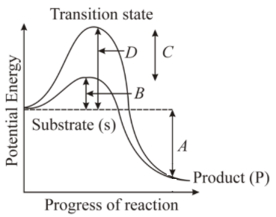
The diagram represents a reaction with and without an enzyme. What of the following labellings represents the activation energy of the enzyme-catalysed reaction?
Match the enzymes in Column I with their respective biochemical reactions in column II. Choose the correct combination from below
| Column I | Column II |
| (P) Transaminases | (i) Removal of a phosphoryl group from a specific amino acid |
| (Q) Protein Kinases | (ii) Removal of α-amino group from a specific amino acid |
| (R) Protein Phosphatases | (iii) Addition of phosphoryl group to a specific amino acid |
| (S) Dehydrogenases | (iv) Interconversion of optical isomers |
| (v) Oxidation and reduction of substrates |
Which group of enzymes catalyses reactions involving a structural rearrangement of a molecule?
Which among the following enzymes, help in joining the molecules together?
Which of the following is a cofactor of carboxypeptidase, a proteolytic enzyme?
Name the organism from the options that produces the enzyme cellulase.
When RNAse enzyme is denatured by adding urea, which ONE of the following combinations of bonds would be disrupted?
Transition state structure of the substrate formed during an enzymatic reaction is
Out of the following, which is correct w.r.t competitive inhibitors?
Enzymes that catalyse interconversion of optical, geometrical or positional isomers are
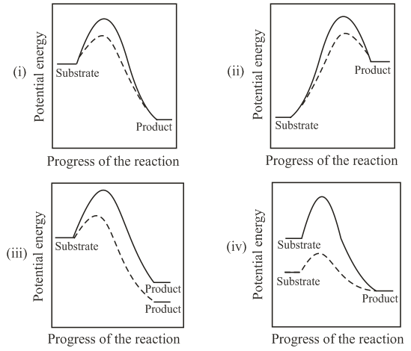
The following graphs with the solid and dotted lines correspond to the reactions without and with enzyme, respectively. Which of the following graph(s) correctly represents the concept of activation energy?
Ethanol is used to treat methanol toxicity because ethanol
Solid and dotted lines represent the activities of pepsin and salivary amylase enzymes of the digestive tract, respectively. Which one of the following graphs best represents their activity vs pH?
Which class of the enzyme catalyses the oxidation nd reduction reactions?
