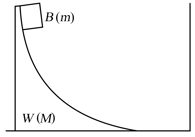
In the figure, the block of mass starts from rest at the top of a wedge of mass All surfaces are without friction. can slide on the ground. slides down onto the ground, moves along it with a speed has an elastic collision with the wall, and climbs back on to


Important Questions on Impulse and Collision
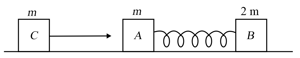
Two blocks and of masses and respectively placed on a smooth floor are connected by a spring. A third body of mass moves with velocity along the line joining and and collides elastically with At a certain instant of time after collision it is found that the instantaneous velocities of and are same then
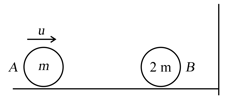
The wall is at extreme right is fixed as shown in figure. Coefficient of restitution for collision between two balls is and between ball and wall is Then speed of A and B after all possible collisions are
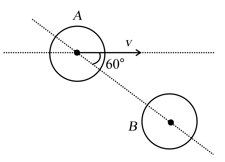
A smooth sphere of mass collides elastically with an identical sphere at rest. The velocity of before collision is in a direction making with the line of centres at the time of impact.
A particle of mass makes an elastic head-on collision with a stationary particle of mass If initial kinetic energy is moving particle is , then during the impact,
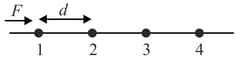
The diagram shows a string of equally placed beads of mass , separated by distance . The beads are free to slide without friction on a thin wire. A constant force acts on the first bead initially at rest till it makes collision with the second bead. The second bead then collides with the third and so on. Suppose that all collisions are elastic.