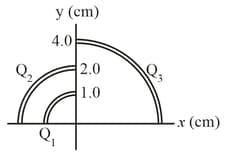
In the figure, three thin plastic rods form quarter-circles with a common center of curvature at the origin. The uniform charges on the three rods are and What is the net electric potential at the origin due to the rods?


Important Questions on Electric Potential
Two tiny metal spheres and , mass and , have equal positive charge The spheres are connected by a massless nonconducting string of length which is much greater than the radii of the spheres.
(a) What is the electric potential energy of the system?
(b) Suppose you cut the string. At that instant, what is the acceleration of each sphere?
(c) A long time after you cut the string, what is the speed of each sphere?
Particle (with a charge of ) and particle (with a charge of ) are fixed in place with separation on the -axis shown in Fig.(a) Particle can be moved along the -axis to the right of particle Figure (b) gives the electric potential energy of the three-particle system as a function of the -coordinate of particle The scale of the vertical axis is set by What is the charge of particle
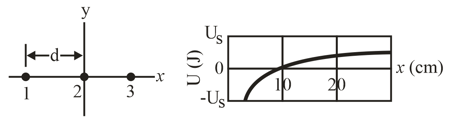
(a) (b)
(a) What is the escape speed for an electron, initially at rest, on the surface of a sphere with radius and a uniformly distributed charge of ? That is, what initial speed must the electron have in order to reach an infinite distance from the sphere and have zero kinetic energy when it gets there?
(b) If its initial speed is twice the escape speed, what is its kinetic energy at infinity?
Proton in a well. The figure shows electric potential along an -axis. The scale of the vertical axis is set by A proton is to be released at with initial kinetic energy
(a) If it is initially moving in the negative direction of the axis, does it reach a turning point (if so, what is the -coordinate of that point) or does it escape from the plotted region (if so, what is its speed at )?
(b) If it is initially moving in the positive direction of the axis, does it reach a turning point (if so, what is the -coordinate of that point) or does it escape from the plotted region (if so, what is its speed at )?
What are the (c) magnitude and
(d) direction (positive or negative direction of the -axis) of the electric force on the proton if the proton moves just to the left of
What are and the direction, if the proton moves just to the right of
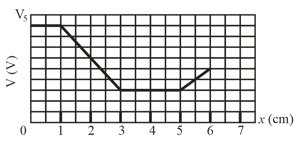
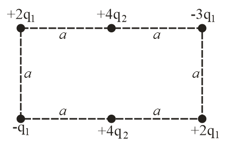
Figure given below shows a rectangular array of charged particles fixed in place, with distance and the charges shown as integer multiples of and . With at infinity, what is the net electric potential at the rectangle's centre? (Hint: Thoughtful examination of the arrangement can reduce the calculation.)