Light guidance in an optical fiber can be understood by considering a structure comprising of thin solid glass cylinder of refractive index surrounded by a medium of lower refractive index . The light guidance in the structure takes place due to successive total internal reflections at the interface of the media and as shown in the figure. All rays with the angle of incidence less than a particular value are confined in the medium of refractive index . The numerical aperture (NA) of the structure is defined as .
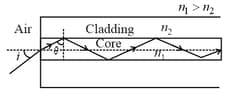
If two structures of same cross-sectional area, but different numerical apertures and are joined longitudinally, the numerical aperture of the combined structure is


Important Questions on Ray Optics
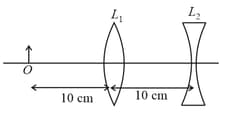
An extended object is placed at point , in front of a convex lens and a concave lens is placed behind it, as shown in the figure. The radii of curvature of all the curved surfaces in both the lenses are . The refractive index of both the lenses is . The total magnification of this lens system is:
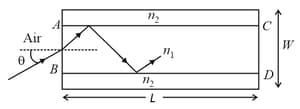
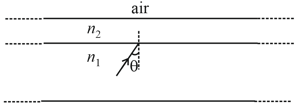
A wide slab consisting of two media of refractive indices and is placed in air as shown in the figure. A ray of light is incident from medium to at an angle , where is slightly larger than . Take refractive index of air as . Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
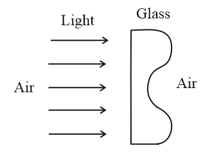
A parallel beam of light strikes a piece of transparent glass having cross section as shown in the figure below. Correct shape of the emergent wavefront will be (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)
[Speed of light