Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
Column I
Column II
(P)
Expansion of metals on heating
(i)
Neither physical nor chemical change
(Q)
A stone kept in the sunlight
(ii)
Chemical change
(R)
Burning of a candle
(iii)
Combination of physical and chemical changes
(S)
Curdling of milk
(iv)
Physical change
(P) - (iv), (Q) - (iii), (R) - (ii), (S) - (i)

Important Questions on Physical and Chemical Changes
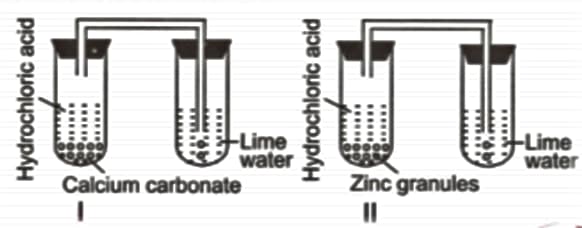
Kanav took two test tubes marked as I and II. In test-tube I, he put calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid while in test-tube II, he put zinc granules and hydrochloric acid. He passed the gas coming out from both the test tubes in lime water. What would be his observation?
Observe the given reaction sequence carefully.
What could and be?
| (i) | (ii) | |
| (A) | ||
| (B) | ||
| (C) | ||
| (D) |
Fill in the blanks by selecting an appropriate option.
When sugar is dissolved in water, it undergoes a (i) change but if sugar is heated in a test tube over the Bunsen burner flame, it first melts, turns brown and finally turns (ii). The new substance formed is (iii) and the change is a (iv) change.
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | |
| (A) | Physical, reversible | Black | Charcoal | Chemical, irreversible |
| (B) | Physical, irreversible | Black | Coal | Chemical, irreversible |
| (C) | Physical, irreversible | Red | Charcoal | Chemical, reversible |
| (D) | Physical, reversible | Red | Coal | Chemical, reversible |
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
| Column I | Column II | |||
| (P) | Dipping iron sheets in molten zinc | (i) | Alloying | |
| (Q) | Prevents the iron surface to come in contact with moisture | (ii) | Galvanisation | |
| (R) | Two or more metals are mixed in a definite ratio to form a homogeneous mixture | (iii) | Tinning | |
| (S) | Coating expensive utensils with tin | (iv) | Painting | |
Study the given figure carefully.
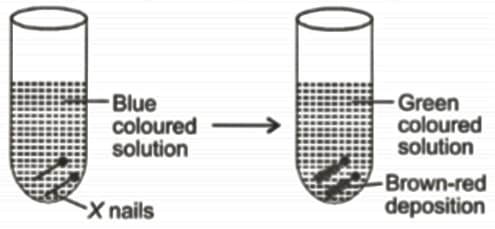
Which of the following reactions explains the above change most appropriately?
I. A gas is produced.
II. Precipitate is formed.
III. State of a substance changes.
IV. A new odour is produced.
V. Shape of a substance changes.
