HARD
Earn 100
Pressure over of a liquid is gradually increased from to , under adiabatic conditions. The final volume of the liquid is . Assuming linear variation of volume with pressure, which of the following is/are correct for this process?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
20% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Chemical Thermodynamics
HARD
Calculate the work done in the following reaction at . State whether work is done on the system or by the system.
EASY
EASY
EASY
(Latent heat of ice is and )
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
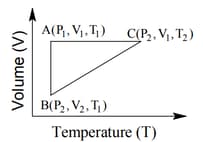
The correct option(s) is (are)
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
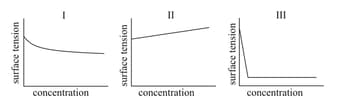
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
fish swimming in water body when taken out from the water body is covered with a film of water of weight . When it is subjected to cooking at , then the internal energy for vaporization in is integer]
[Assume steam to be an ideal gas. Given for water at and bar is ]
MEDIUM
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is
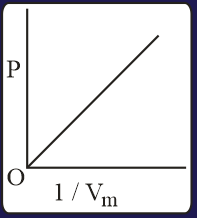
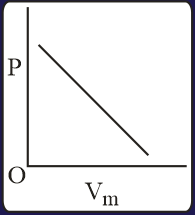
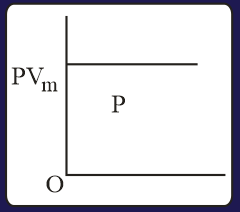
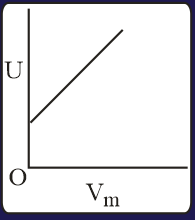
MEDIUM
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) (ln7.5 = 2.01)
HARD
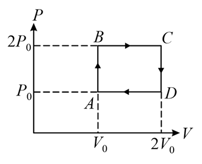
The above diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono-atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle, is:
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM

