Protons and helium nuclei from the Sun pass into the Earth's atmosphere above the poles, where the magnetic flux density is The particles are moving at a speed of at right angles to the magnetic field in this region. The magnetic field can be assumed to be uniform.
(a) Calculate the radius of the path of a proton as it passes above the Earth's pole.
Mass of a helium nucleus
Charge on a helium nucleus
Mass of proton
Charge on proton
Charge on a helium nucleus

Important Questions on Motion of Charged Particles
Protons and helium nuclei from the Sun pass into the Earth's atmosphere above the poles, where the magnetic flux density is The particles are moving at a speed of at right angles to the magnetic field in this region. The magnetic field can be assumed to be uniform.
(b) Sketch a diagram to show the deflection caused by the magnetic field to the paths of a proton and of a helium nucleus that both have the same initial velocity as they enter the magnetic field.
This diagram shows a thin slice of metal of thickness and width . The metal slice is in a magnetic field of flux density and carries a current , as shown.
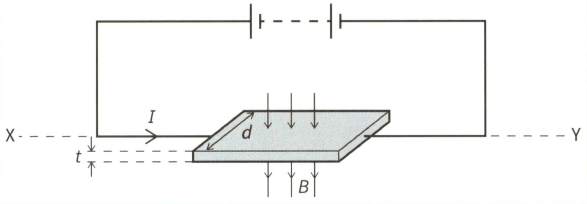
Copy the diagram and mark the slice that becomes negative because of the Hall effect.
This diagram shows a thin slice of metal of thickness and width . The metal slice is in a magnetic field of flux density and carries a current , as shown.
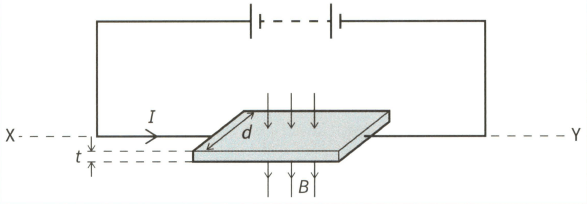
Copy the diagram and mark where a voltmeter needs to be placed to measure the Hall voltage.
This diagram shows a thin slice of metal of thickness and width . The metal slice is in a magnetic field of flux density and carries a current , as shown.
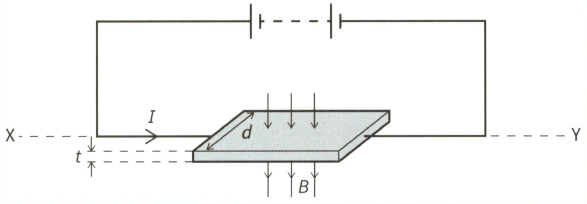
Derive an expression for the Hall voltage in terms of the number density of the charge carriers in the metal and the charge on an electric iron.
This diagram shows a thin slice of metal of thickness and width . The metal slice is in a magnetic field of flux density and carries a current , as shown.
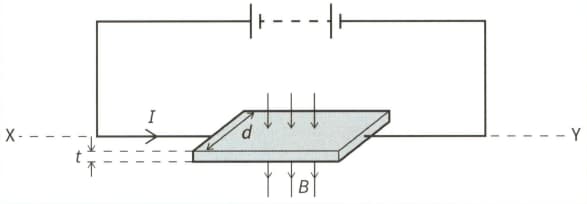
Given that theme an drift velocity v of the free electrons in the metal.
This diagram shows a thin slice of metal of thickness and width . The metal slice is in a magnetic field of flux density and carries a current , as shown.
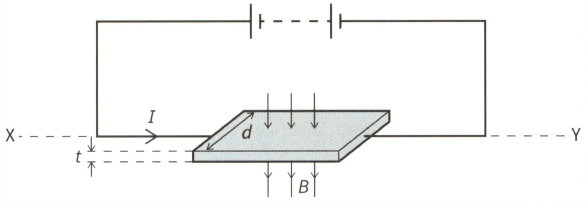
Given that the Hall voltage across the metal slice.
This diagram shows a thin slice of metal of thickness and width . The metal slice is in a magnetic field of flux density and carries a current , as shown.
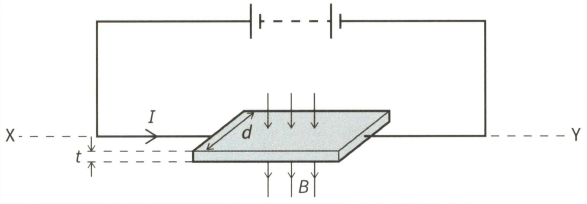
(c) Given that
Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the mean drift velocity v of the electrons, assuming the percentage uncertainties in the quantities are as shown.
This diagram shows a thin slice of metal of thickness and width . The metal slice is in a magnetic field of flux density and carries a current , as shown.
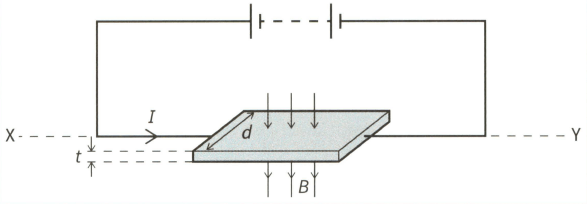
Explain why, in terms of the movement of electrons, the Hall voltage increases when I increase.
