The diagram shows a cup of tea

Which row describes the water particles in the air above the cup compared with the water particles in the cup?
Moving faster
Closer together
A


B

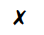
C
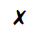

D




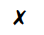
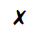

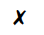
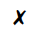

Important Questions on Matter in Our Surroundings
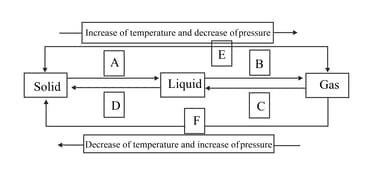
The symbols A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram represent various types of processes for the change of states of matter, namely solid, liquid and gas. Name the processes and then redraw the complete scheme.
(a) What could particles X be?
(b) Name the gas (or mixture of gases) Y.
(c) What is the phenomenon exhibited by particles X known as?
(d) What is causing the movement of particles X?
(e) What conclusion does the existence of this phenomenon give us about the nature of matter?
A student heats a beaker containing ice and water. He measures the temperature of the beaker as a function of time and draws the following graph.
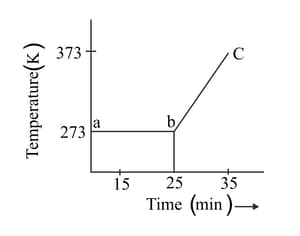
At what temperature and time ice melts?
A student heats a beaker containing ice and water. He measures the temperature of the beaker as a function of time and draws the following graph.
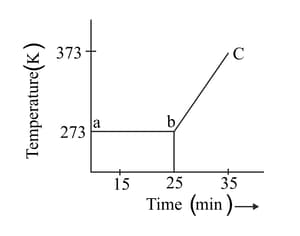
What does the curve bc represent?
Look at the diagram below. Jar A contains a red-brown gas whereas jar B contains a colourless gas. The two gas jars are separated by a glass plate placed between them. After some time when the glass plate is removed it is seen that jar A and jar B turns reddish-brown.
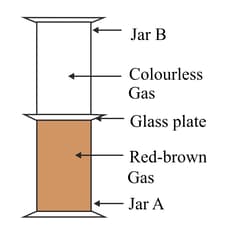
Name one coloured solid and one colourless liquid which can show the same phenomenon.
