The diagram shows the surface of a lake of water. A lamp has been placed on the bottom of the lake.
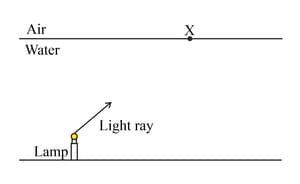
Describe how the direction light ray changes as it enters the air.


Important Questions on Light
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
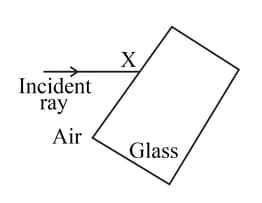
Think about what happens at point X. Draw a normal at X and the path of the refracted ray inside the glass block.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
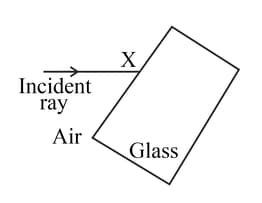
Add the label 'Y' where your first refracted glass ray leaves the glass block.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
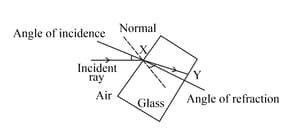
Think about what happens at the point you have labelled Y. Draw a normal at Y and the path of the refracted ray through the air to the right of the glass block.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
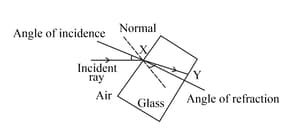
Add the label 'Z ' to the angle of refraction between the normal at Y and the refracted ray.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
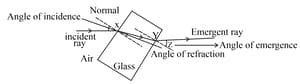
State the connection between the original angle of incidence at point X and the final angle of refraction Z at point Y.
The diagram shows three large coloured lamps arranged one above the other. They shine through a thick glass block onto a screen.
The orange light ray shown hits the block at a right-angle. Complete the ray diagram for the orange light. Label the point on the screen where the ray arrives with the letter 'X'.
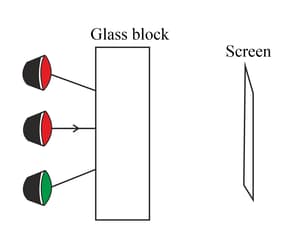
The diagram shows three large coloured lamps arranged one above the other. They shine through a thick glass block onto a screen.
The orange light ray shown hits the block at a right-angle. Complete the ray diagram for the orange light. Label the point on the screen where the ray arrives with the letter 'X'.
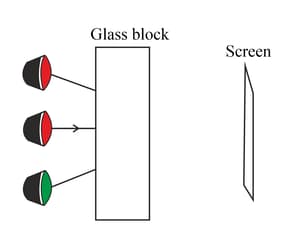
Add rays for the red and green lamps to show rays that also arrive at point 'X'.
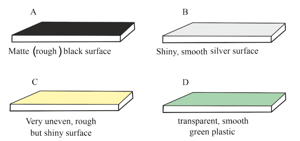
Look at the diagram showing different surfaces. Predict what will be observed when light falls on each surface. Complete the table with your answers.