The energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction is different from that for an endothermic reaction. The following keywords/phrases will be needed to fill in the information boxes accompanying the diagrams.
given out positive taken in reactants negative products
Exothermic reactions:
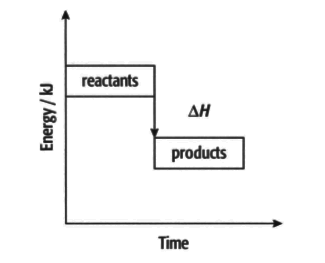
Use information from the diagram and the keywords/phrases to complete the following information.
In an exothermic reaction, the _____ have more energy than the _____. This means that is _____. The difference in energy is _____ as heat. The temperature of the surroundings increases/decreases. (Delete the incorrect word)


Important Questions on How Far? How Fast
The energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction is different from that for an endothermic reaction. The following keywords/phrases will be needed to fill in the information boxes accompanying the diagrams.
given out positive taken in reactants negative products
Endothermic reactions:
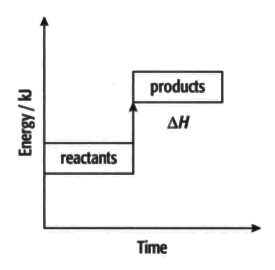
Use information from the diagram and the keywords/phrases to complete the following information.
In an endothermic reaction, the _____ have more energy than the _____. This means that is _____. The difference in energy is _____ as heat. The temperature of the surroundings increases/decreases. (Delete the incorrect word)
Complete the following table from your understanding of the factors that affect the speed (rate) of a reaction.
| Factor affecting the reaction | Types of reaction affected | Change made in the condition | Effect on the rate of reaction |
| Concentration | All reactions involving solutions or reactions involving gases. |
An increase in the concentration of one, or both, of the ____ means there are more particles in the same volume. |
Increases the rate of reaction as the particles _____ more frequently. |
Complete the following table from your understanding of the factors that affect the speed (rate) of a reaction.
| Factor affecting the reaction | Types of reaction affected | Change made in the condition | Effect on the rate of reaction |
| Pressure | Reactions involving _____ only. |
An increase in the pressure. |
Greatly _____ the rate of reaction. The effect is same as that of an increase in _____. |
Complete the following table from your understanding of the factors that affect the speed (rate) of a reaction.
| Factor affecting the reaction | Types of reaction affected | Change made in the condition | Effect on the rate of reaction |
| Temperature | All reactions |
An increase in temperature — this means that molecules are moving _____ and collide more _____, the particles also have more _____ when they collide. |
_____ the rate of reaction. |
Complete the following table from your understanding of the factors that affect the speed (rate) of a reaction.
| Factor affecting the reaction | Types of reaction affected | Change made in the condition | Effect on the rate of reaction |
| Particle size | Reactions involving solids and liquids, solids and gases or mixtures of solids. |
Use the same mass of a solid but make the pieces of solid _____. |
Greatly increases the rate of reaction. |
Complete the following table from your understanding of the factors that affect the speed (rate) of a reaction.
| Factor affecting the reaction | Types of reaction affected | Change made in the condition | Effect on the rate of reaction |
| Light | a number of photochemical reactions including photosynthesis, the reaction between methane and chlorine, and the reaction on photographic film. | Reaction in the presence of _____ or UV. | greatly increases the rate of reaction. |
Complete the following table from your understanding of the factors that affect the speed (rate) of a reaction.
| Factor affecting the reaction | Types of reaction affected | Change made in the condition | Effect on the rate of reaction |
| Using a catalyst | Slow reactions can be speeded up by adding a suitable catalyst. |
Reduces the amount of _____ required for the reaction to take place. The catalyst is present in the same _____ at the end of the reaction. |
_____ the rate of reaction. |
What is global warming, and why is it a problem?
