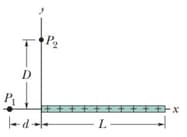
The figure shows a thin plastic rod of length and uniform charge .
(a) In terms of distance , find an expression for the electric potential at a point .
(b) Next, substitute variable for and find an expression for the magnitude of the component of the electric field at
(c) What is the direction of relative to the positive direction of the -axis?
(d) What is the value of at for
(e) From the symmetry in figure determine at .


Important Questions on Electric Potential
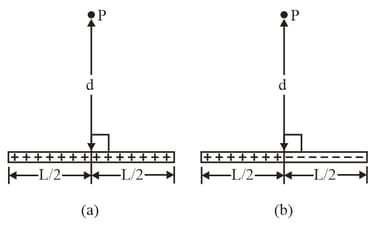
(a) Figure shows a nonconducting rod of length and uniform linear charge density . Assume that the electric potential is defined to be at infinity. What is at point at a distance along the rod's perpendicular bisector?
(b) Figure shows an identical rod except that one half is now negatively charged. Both halves have a linear charge density of magnitude . With at infinity, what is at Is the potential at positive, negative or zero if is moved in the plane of the figure by a distance of (c) upward and (d) leftward?
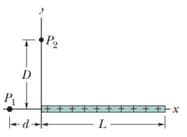
The thin plastic rod of length as shown in figure, has a non-uniform linear charge density where, (a) With at infinity, find the electric potential at point on the -axis at (b) Find the electric field component at (c) Why cannot the field component at be found using the result of (a)?
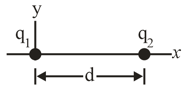
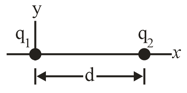
In the figure, particles with the charges and are fixed with a separation of With electric potential defined to be at infinity, what are the finite (a) positive and (b) negative values of at which the net electric potential on the -axis is zero?
Two particles of charges and are separated by a distance in the figure. The net electric field due to the particles is zero at
(a) With at infinity, locate (in terms of ) any point on the -axis (other than at infinity) at which the electric potential due to the two particles is zero.
(b) If, instead the net electric potential is at find (in terms of ) the coordinates of any point (other than at infinity) at which the net electric field is zero.
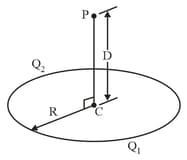
Plastic rod has been bent into a circle of radius It has a charge uniformly distributed along one quarter of its circumference and a charge is uniformly distributed along the rest of the circumference (as shown in fig.) With at infinity, what is the electric potential at (a) the center of the circle and (b) point on the central axis of the circle at distance from the center?
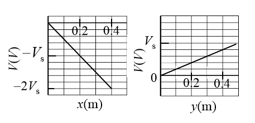
An electron is placed in an plane where the electric potential depends on and as shown, for the coordinate axes, in the figure (the potential does not depend on ). The scale of the vertical axis is set by . In unit-vector notation, what is the electric force on the electron?
The electric potential in the space between two flat parallel plates and is (in volts), where, (in meters) is the perpendicular distance from plate At
(a) What is the magnitude of the electric field?
(b) Is the field directed towards or away from plate
