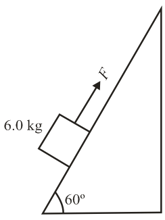
The given figure shows a block on a ramp with a coefficient of static friction of . A force is applied up the ramp. What magnitude of that force puts the block on the verge of sliding down the ramp?


Important Questions on Force and Motion-II
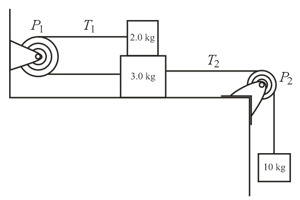
In the figure shown below, a block is placed on the top of a block, which lies on a frictionless surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the two blocks is . They are connected via a pulley and a string. A hanging block of mass is connected to the block via another pulley and string. Both the strings have negligible mass and both pulleys are frictionless and have negligible mass. When the assembly is released, what are
(a) the acceleration magnitude of the blocks? (b) the tension in string ? and (c) the tension in string ? (Take )
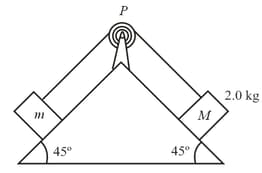
The figure shows a block of mass connected to a block of mass , both on inclined planes where the coefficient of static friction is , Find the minimum and maximum values of for which the system is at rest.
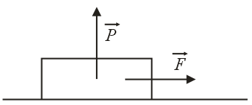
A block is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force of magnitude and a vertical force are applied to the block (given in the below figure). The coefficients of friction for the block and surface are and , respectively. Determine the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the block if the magnitude of is (a) (b) and (c) .
A person pushes horizontally with a force of on a crate to move it across a level floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction is . What is the magnitude of
(a) the frictional force and
(b) the crate's acceleration?
The mysterious sliding stones. Along the remote Racetrack Playa in Death Valley, California, stones sometimes gouge out prominent trails in the desert floor, as if the stones had been migrating (given in the below figure). For years curiosity mounted about why the stones moved. One explanation was that the strong winds during occasional rainstorms would drag the rough stones over ground softened by rain. When the desert dried out, the trails behind the stones were hard-baked in place. According to the measurements, the ground is about . What horizontal force must act on a stone (a typical mass) to maintain the stone's motion once a gust has started it moving?
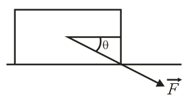
A block is pushed along a horizontal floor by a force of magnitude at an angle with the horizontal (in the given below figure). The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor is . Calculate the magnitudes of
(a) the frictional force on the block from the floor and (b) the block's acceleration.