The modern or long form of the periodic table is based on the modern periodic law. The table is the arrangement of elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers. The modern periodic table is the present form of the periodic table. And it consists of vertical columns and horizontal rows.
The teacher took a lesson on the modern periodic table in the classroom. One table with some information is already given to students. And she asked them to answer the following questions.

Group 15
Group 16
Group 17
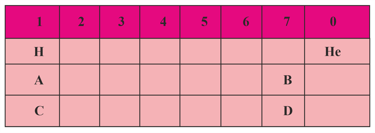
D
__
A
__
B
C
Elements A, B, C and D belong to groups of the periodic table as shown in the table above.
(i) Is C a metal or non-metal?
(ii) Which is more reactive, C or A?
(iii) Which will be smaller, B or C?
(iv) Name the family to which A belongs.
(v) What is the valency of B.
(vi) The formula of the delta formed between D and C.


(i) Is C a metal or non-metal?
(ii) Which is more reactive, C or A?
(iii) Which will be smaller, B or C?
(iv) Name the family to which A belongs.
(v) What is the valency of B.
(vi) The formula of the delta formed between D and C.

Important Questions on Periodic Classification of Elements
Classification of things makes it easier to organise, identify or study them. Since a long time ago the known elements were classified into metals and non-metals. The discoveries of new elements expanded the perception of the scientists that not all metals or non-metals possess the same property. Every metal is different from the other in some way or the other. Though their physical properties are the same, but chemical properties are not the same and vice versa. It was then tough to study the properties of every element.
There were few scientists named Dobereiner, Lothar Meyer and Newlands who attempted to classify the elements. It was clear from their attempts that elements show periodicity in their properties. Periodicity is the term used for the repeating of something after particular intervals. On Mendeleev began arranging the elements and comparing them by their atomic weights and arranged them in a tabular representation which proposed the idea of the first periodic table of elements. The modern periodic table is an arrangement of the chemical elements and is organised on the basis of their atomic numbers. The law of periodicity that is related to atomic numbers was proposed by Henry Moseley.

Rupali has been provided with five elements A, B, C, D and E with atomic numbers and and Aviral with five elements P, Q, R, S and T with atomic numbers and .
Find out the pairs of elements from the two groups of elements that will exhibit similar chemical properties.
| Group/Periods | 1 | 2 | 3 to 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | A | B | C | ||||||
| 3 | D | E | F |
Using the above table, answer the following questions:
(i) Which element will be from only covalent compounds?
(ii) Which element is a metal with valency 2?
(iii) Which element is a non-metal with valency 3?
(iv) Out of D and E, which one has a bigger atomic radius and why?
(v) Write the common names for the families of elements, C and F.
For the main groups of the periodic table, the metallic properties of the elements vary approximately with their position as shown in the chart below
(a) Where will you find the most metallic element?
(b) Where will you find the most nonmetallic element?
(c) Where will you find the smallest atom?
| Group 16 | Group 17 |
|---|---|
(b) State whether C is more reactive or less reactive than A.
(c) Will C be larger or smaller in size than B?
(d) Which type of ion, cation or anion, will be formed by element A?
