The period of a simple pendulum is related to its length by the equation:
A graph is plotted with on the -axis and on the -axis. Express the gradient in terms of .

Important Questions on Practical Skills at A Level
The time period of a simple pendulum is related to its length by the equation:
Where is the acceleration of free fall.
A student measures the time for oscillations for different lengths . This table shows her data.
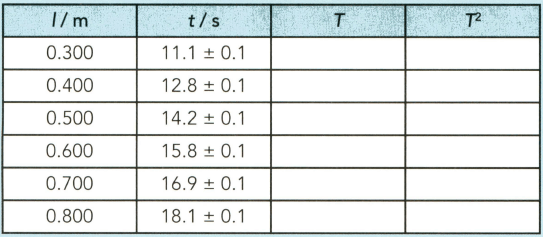
(i) Calculate and record values of , including the absolute uncertainties in .
The time period of a simple pendulum is related to its length by the equation:
Where is the acceleration of free fall.
A student measures the time for oscillations for different lengths . This table shows her data.

Plot a graph of against including error bars for .
The time period of a simple pendulum is related to its length by the equation:
Where is the acceleration of free fall.
A student measures the time for oscillations for different lengths . This table shows her data.

Draw a straight line of best fit and a worst acceptable line on your graph.
The period of a simple pendulum is related to its length by the equation:
Where is the acceleration of free fall.
A student measures the time for oscillations for different lengths . This table shows her data.
Determine the gradient of your line and include the uncertainty in your answer.
The period of a simple pendulum is related to its length by the equation:
Where is the acceleration of free fall.
A student measures the time for oscillations for different lengths . This table shows her data.
Use your value of the gradient to determine and include the absolute uncertainty in your value.
The period of a simple pendulum is related to its length by the equation:
Where is the acceleration of free fall.
A student measures the time for oscillations for different lengths . This table shows her data.

Using the value of and its uncertainty, calculate the value of when the length is . Include the absolute uncertainty in your answer.
Readings are taken of the resistance of a thermistor at different temperatures . It is suggested that the relationship between and is , where and are constants. A graph is plotted with on the y-axis and on the x-axis. State the value of the gradient and the y-intercept in terms of and .
Readings are taken of the resistance of a thermistor at different temperatures . It is suggested that the relationship between and is , where and are constants. Values for and are shown in the given table:
Complete the table and include absolute uncertainties in .
