To allow for expansion in the summer when temperatures rise, a steel railway line laid in cold weather is pre-stressed by applying a force of to the rail of cross-sectional area If the railway line is not pre-stressed, a strain of is caused by each degree Celsius rise in temperature. The Young modulus of the steel is .
(b) Calculate:
(ii) The temperature rise when the rail becomes unstressed.

Important Questions on Matter and Materials
This is a stress- strain graph for a metal wire.
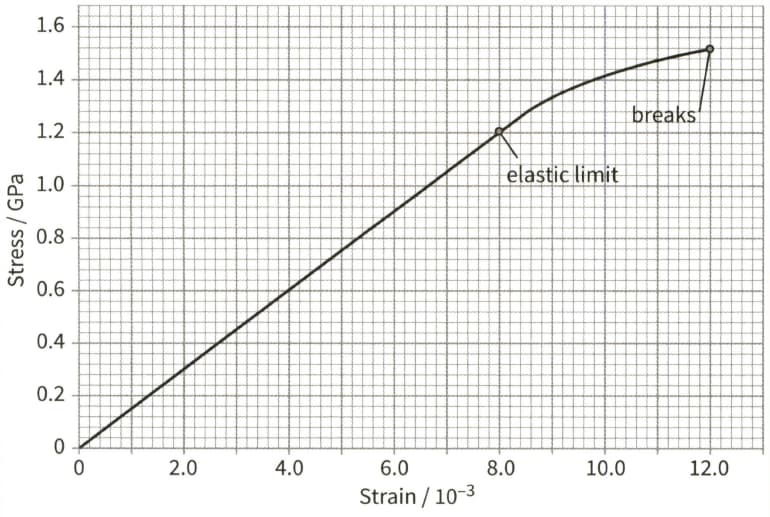
The wire has a diameter of and a natural length of . Use the graph to determine:
(a) The Young modulus of the wire
This is a stress- strain graph for a metal wire.
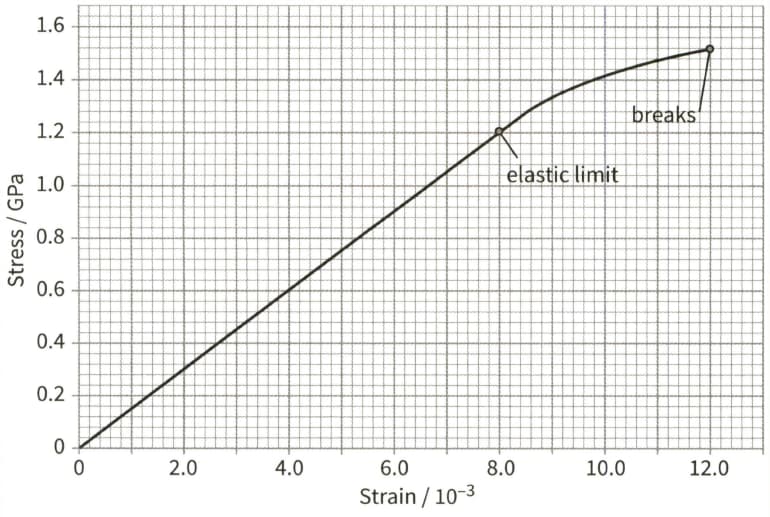
The wire has a diameter of and a natural length of . Use the graph to determine:
(b) The extension of the wire when the stress is 0.60GPa
This is a stress- strain graph for a metal wire.
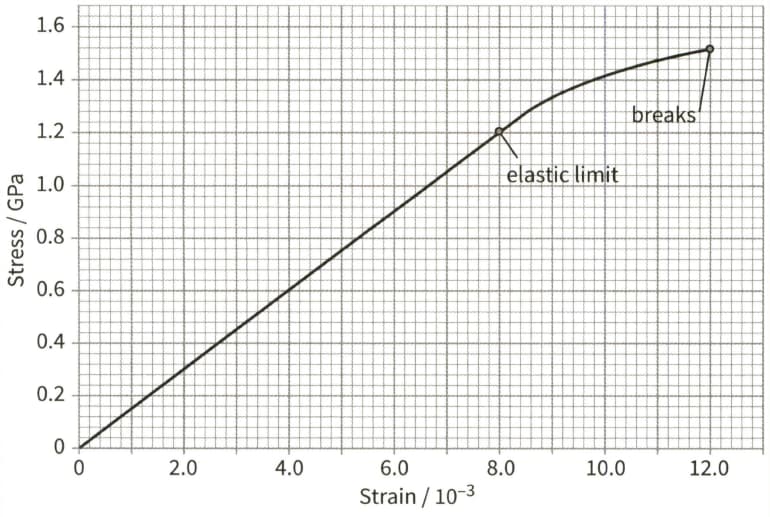
The wire has a diameter of and a natural length of . Use the graph to determine:
(c) the force that causes the wire to break, assuming that the cross-sectional area of the wire remains constant
This is a stress- strain graph for a metal wire.
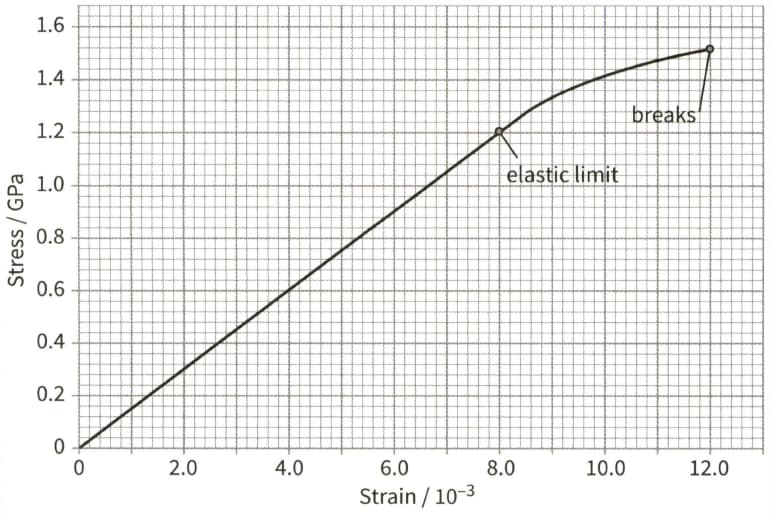
The wire has a diameter of and a natural length of . Use the graph to determine:
(d) the energy density when the wire has a stress of 0.60GPa.
This is a force-extension graph for a spring.
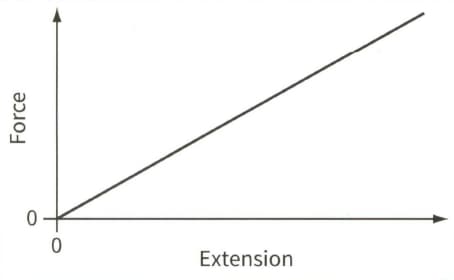
(a) State what is represented by:
(i) The gradient of the graph
This is a force-extension graph for a spring.

(b) The spring has force constant . The spring is compressed by , within the limit of proportionality, and placed between two trolleys that run on a friction-free, horizontal track. Each trolley has a mass of . When the spring is released the trolleys fly apart with equal speeds but in opposite directions.
(ii) Explain why the two trolleys must fly apart with equal speeds.
This is a force-extension graph for a spring.
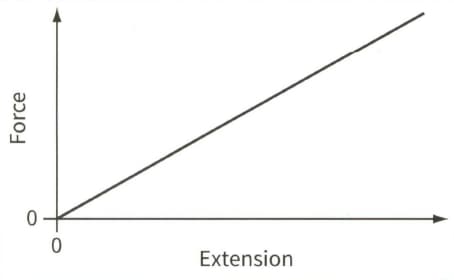
(b) The spring has force constant . The spring is compressed by , within the limit of proportionality, and placed between two trolleys that run on a friction-free, horizontal track. Each trolley has a mass of . When the spring is released the trolleys fly apart with equal speeds but in opposite directions.
(iii) Calculate the speed of each trolley.
(a) Liquid of density fills a cylinder of base area and height . Using the symbols, state the mass of liquid in the container.
