Two particles, an particle and a particle, are travelling through a uniform magnetic field. They have the same speed and their velocities are at right angles to the field. Determine the ratio of:
(b) the charge of the particle to the charge of theparticle.

Important Questions on Motion of Charged Particles
Two particles, an -particle and a -particle, are travelling through a uniform magnetic field. They have the same speed and their velocities are at right angles to the field. Determine the ratio of:
(c) the force on the -particle to the force on the -particle
Two particles, an -particle and a -particle, are travelling through a uniform magnetic field. They have the same speed and their velocities are at right angles to the field. Determine the ratio of:
(d) the radius of the -particle's orbit to the radius of the -particle's orbit.
This diagram shows the path of an electron as it travels in air. The electron rotates clockwise around a uniform magnetic field into the plane of the paper, but the radius of the orbit decreases in size.

(a) (i) Explain the origin of the force that causes the electron to spiral in this manner.
This diagram shows the path of an electron as it travels in air. The electron rotates clockwise around a uniform magnetic field into the plane of the paper, but the radius of the orbit decreases in size.

(a) (ii) Explain why the radius of the circle gradually decreases.
This diagram shows the path of an electron as it travels in air. The electron rotates clockwise around a uniform magnetic field into the plane of the paper, but the radius of the orbit decreases in size. Figure.

(b) At one point in the path, the speed of the electron is and the magnetic flux density is Calculate:
(i) the force on an electron at this point due to the magnetic field.
This diagram shows the path of an electron as it travels in air. The electron rotates clockwise around a uniform magnetic field into the plane of the paper, but the radius of the orbit decreases in size.

(b) At one point in the path, the speed of the electron is and the magnetic flux density is Calculate:
(ii) the radius of the arc of the circular path at this point.
This diagram shows an arrangement to deflect protons from a source to a detector using a magnetic field. The charge on each proton is A uniform magnetic field exists only within the area shown. Protons move from the source to the detector in the plane of the paper.
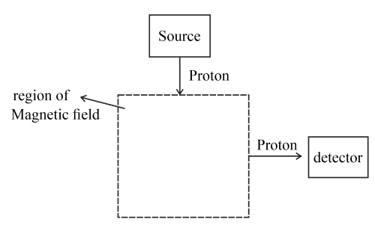
(a) (i) Copy the diagram and sketch the path of a proton from the source to the detector. Draw an arrow at two points on the path to show the direction of the force on the proton produced by the magnetic field.
