EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
What can be concluded about the value of and from this graph?
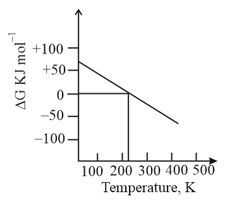

(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
The fat, glyceryl trioleate, is metabolized via the following reaction. Given the enthalpies of formation, calculate the energy liberated when of this fat reacts.
(Atomic weights: )
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Using the enthalpies of formation, calculate the energy released when of reacts according to the following equation.
(Atomic weights: )
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Calculate the heat of combustion of propane, using the listed standard enthalpy of reaction data:
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Calculate the value of for the following reaction using the listed thermochemical equations:
