MEDIUM
Earn 100
What is hemicellulose?
Important Questions on Chemical Constituents of Living Cells
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
A) In a polysaccharide chain, the right end is reducing end and the left end is non-reducing end.
B) In a protein, the right end is a first amino acid called N-end, and the left end is called C-terminal.
C) Concanavalin A is a drug used to cure cancer along with vinblastin and curcumin.
D) GLUT- enables glucose transport into cells.
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
Assertion Starch can hold iodine molecules whereas cellulose cannot hold iodine molecules.
Reason Cellulose forms helical secondary structures whereas starch does not contain complex helices.
The correct answer is:
EASY
Identify the product of the following reaction.
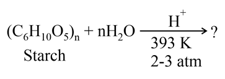
MEDIUM
Give the plausible explanation for the following:
Starch and cellulose both contain glucose unit as monomer, yet they are structurally different.
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
The structure of the following polymer is:
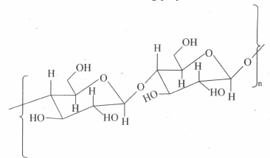
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
| Column I (Biological molecules) |
Column II (Functions) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| A. | Glycogen | p. | Hormone |
| B. | Globulin | q. | Biocatalyst |
| C. | Steroids | r. | Antibody |
| D. | Thrombin | s. | Storage product |
HARD
EASY

