Why is the induced emf in a coil zero when its plane is normal to the magnetic field even though maximum magnetic flux is linked with the coil in this position?

Important Questions on Electromagnetic Induction
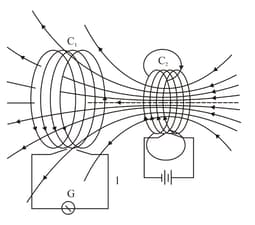
Figure 6.51 shows two coils and placed facing each other. The steady current in coil produces a steady magnetic field. Whenever the coil is moved towards or away from it, a current is induced in as indicated by the deflection in the galvanometer.
Answer the following question:
What would you do to obtain a large deflection of the galvanometer?
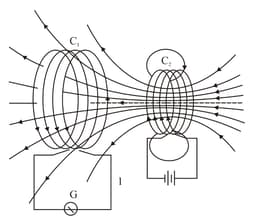
Figure 6.51 shows two coils and placed facing each other. The steady current in coil produces a steady magnetic field. Whenever the coil is moved towards or away from it, a current is induced in as indicated by the deflection in the galvanometer.
Answer the following question:
How would you demonstrate the presence of an induced current in the absence of a galvanometer?
A current is induced in coil due to the motion of current-carrying coil . Write any two ways by which a large deflection can be obtained in the galvanometer .
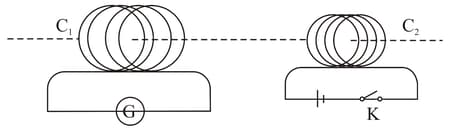
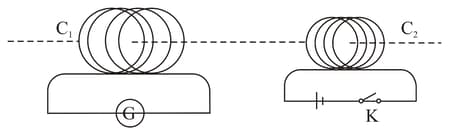
A current is induced in coil due to the motion of current-carrying coil . Suggest an alternative device to demonstrate the induced current in place of galvanometer.
A magnet is quickly moved in the direction indicated by an arrow between two coils
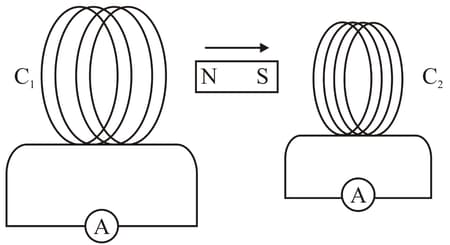
and as shown in Fig. 6.53. What will be the direction of induced current in each coil as seen from the magnet? Justify your answer.
