Write two application of Ohm's law in daily life.
Important Questions on Electric Current
Write Ohm's law. Draw a circuit diagram to prove it experimentally in the laboratory.
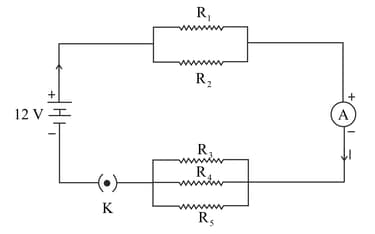
In figure and a battery is connected to the arrangement. Calculate:
(a) Total resistance in the circuit.
(b) Total current flowing in the circuit.
The potential difference between the two ends of a conductor is , and the current flowing through the conductor is . At a constant temperature, which of the following statement is true for the conductor?
Establish relation between potential difference and electric current by plotting graph.
How is the concept of resistance obtained from Ohm's law?
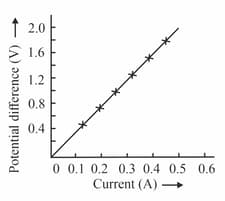
A graph for a nichrome wire is given below. What do you infer from this graph? Draw a labelled circuit diagram to obtain such a graph.
A current of flows when an electric bulb is connected to mains. What would be the current when the same bulb is connected to a main?
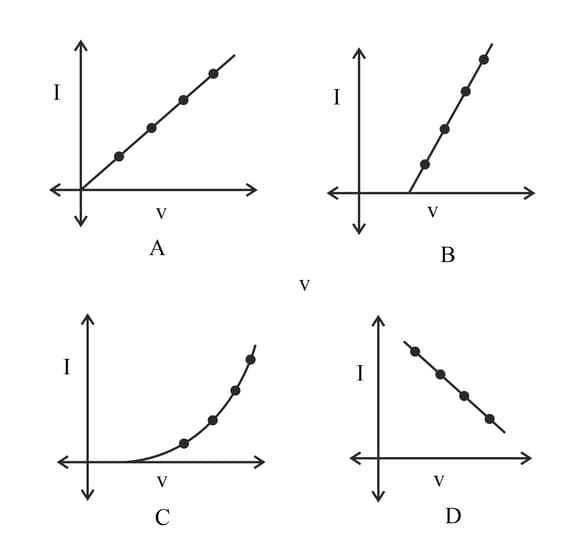
Following figures shows graph of . Which graph is correct according to Ohm's law?
The values of current () flowing through a given resistor of resistance (), for the corresponding values of potential difference () across the resistor, are as given below:
| (volts) | ||||||||
| (amperes) |
Plot a graph between current () and potential difference () and determine the resistance () of the resistor.

