Hardy-Weinberg Principle
Important Questions on Hardy-Weinberg Principle
Which type of selection is industrial melanism observed in moth, Biston betularia?
For the MN-blood group system, the frequencies of M and N alleles are 0.7 and 0.3, respectively. The expected frequency of MN-blood group bearing organisms is likely to be:
Appearance of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is an example of
represents an equation used in
In a large, randomly mating population, only one person in 10,000 is an albino. What will be the frequency of a carrier person of albinism?
In a long term experiment on a population of Drosophila melanogaster, the frequency of two alleles 'a' and 'b' of a multi-allelic locus X over time has been shown in the following graph.
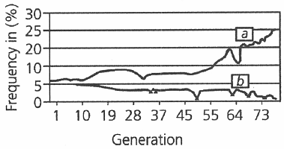
6 students were asked to evaluate the observed pattern and their inferences are given below.
Student 1: Environment is not uniformly selective.
Student 2: Population may be under artificial selection.
Student 3: Genetic variability is progressively reduced.
Student 4: Genetic variability is progressively increased.
Student 5: Mechanism such as genetic drift is operating from time to time.
Student 6: Selection is favouring a particular genotype through directional selection.
The appropriate conclusions were drawn by
**Formatting error resolved. Scientific name was changed in Italics.**
Following table shows data on amino acid substitution in the chain of haemoglobin in four different mammalian species A, B, C and D. On the basis of the data shown in the table, choose the most appropriate evolutionary tree from those given below.
|
Comparison of Species |
Number of Amino Acid Substitution |
| A and B | 19 |
| B and C | 26 |
| A and C | 27 |
| D and C | 27 |
| A and D | 20 |
| D and B | 1 |
Study the characteristic of a population represented in the graph below:
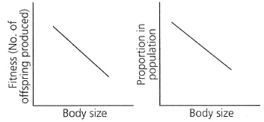
Which type of selection, this population is likely to undergo?
Mark the correct graph that represents the type of selection that this population is likely to undergo.

Stabilising selection favours
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
(i) Increase in melanised moths after industrialisation in Great Britain is a proof for natural selection.
(ii) When more individuals of a population acquire a mean character value, it is called disruption.
(iii) Changes in allelic frequency in a population will lead to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
(iv) Genetic drift changes the existing gene or allelic frequency in future generations.
The given graph shows the range of variation among population members for a trait determined by multiple gene. If the population is subjected to disruptive selection for several generations, which of the following distributions is most likely to result?
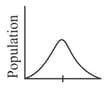
The factors involved in the formation of new species are:
An isolated population of humans with approximately equal numbers of blue-eyed and brown-eyed individuals was decimated by an earthquake. Only a few brown-eyed people remained to form the next generation. This kind of change in the gene pool is called a:
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option.
- When migration of a section of population occurs, change in the original as well as in the new population. New genes/alleles are added to the population and these are lost from the population. There would be a if this gene migration, happens multiple times. If the same change occurs by chance, it is called . Sometimes the change in allele frequency is so different in the new sample of population that they become a different species. The original drifted population becomes founders and the effect is called .
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (v) | (vi) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | new | old | ||||
| (b) | old | new | ||||
| (c) | new | old | ||||
| (d) | old | new |
The effects of genetic drift are more marked in
Match Column I with Column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation | Changes in population’s frequencies due to chance alone | ||
| Gene flow | Differences in survival and reproduction among variant individuals | ||
| Natural selection | Immigration, emigration change allele frequencies | ||
| Genetic drift | Source of new alleles |
The Hardy-Weinberg principle cannot operate if
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is known to be affected by gene flow, genetic drift, mutation, genetic recombination and
At a particular locus, frequency of allele is and that of allele is . What would be the frequency of heterozygotes in a random mating population at equilibrium?

