Genetic Disorders
Genetic Disorders: Overview
Genetic disorders are the diseases that are transmitted from one generation to other without any alteration. This topic discusses Mendelian disorders and chromosomal disorders.
Important Questions on Genetic Disorders
Choose the Mendelian disorder that is a sex-linked recessive disorder.
Which of the following species is rarely haemophilic?
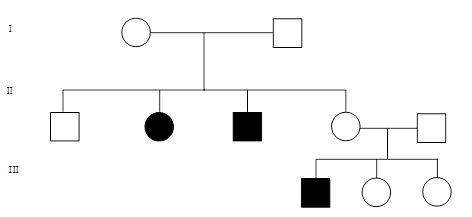
The trait can be described as:
The haemophilia is:
Sickle cell anaemia is characterised by
XO chromosomal abnormality in humans causes _____.
Genes of which one of the following is present exclusively on the X-chromosome in humans?
Choose the correct the combination.
| Group I | Group II | ||
| P. | Phenylketonuria | i. | Melanin synthesis |
| Q. | Albinism | ii. | Conversion of Phenylalanine to Tyrosine |
| R. | Homocystinuria | iii. | Tyrosine degradation |
| S. | Argininemia | iv. | Methionine metabolism |
| v. | Urea synthesis |
Fill in the blank with the correct option given in the bracket.
_____ (Phenylalanine hydroxylase/Phenyl oxygenate) is not synthesized in phenylketonuria disease?
Which of the following is/are sex-linked disease?
The progeny of normal woman and colour-blind father will be
Which of the following statements are correct?
Due to non-disjunction of chromosomes during spermatogenesis, sperms carry both sex chromo-somes (22 A + XY) and some sperms do not carry any sex chromosome (22 A + O). If these sperms fertilise normal eggs (22 A + X), what type of genetic disorders appear among the offspring ?
The X/O syndrome is called Turner’s syndrome.
Sickle-cell anaemia, the best example of natural selection, is due to gene modification related to amino acid of first or second beta chain?
How many chromosomes may be present in Klinefelter syndrome?
Which ONE of the following Mendelian diseases is an example of -linked recessive disorder?
In sickle cell anaemia there is deformity of :
Down syndrome is the result of monoploidy.
Which of the following is a genetic disease?
