Human Excretory System
Human Excretory System: Overview
This topic describes the human excretory system. The human excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. It discusses the structures of the excretory system in detail.
Important Questions on Human Excretory System
Formation of concentrated (hyperosmotic) urine in vertebrates generally depends on
Name the two types of urinary sphincter muscles. Where are these located?
The flow of urine into the urinary bladder is controlled by urinary sphincters.
The internal urinary sphincter is under involuntary control whereas the external sphincter is under voluntary control.
Column of Bertini are found in the liver.
Identify A and B from the given diagram.
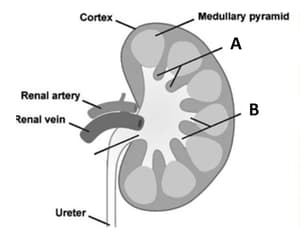
What are the columns of Bertin in the kidneys?
What drains the major Calyx?
The major calyx surrounds the apex of the malpighian pyramids.
The walls of renal pelvis consists of a mucosal lining of _____ epithelium.
State the function of major and minor calyses.
Explain how major calyx is formed?
Minor calyx surrounds renal _____ (papillae/tubule) of each pyramid.
Write one difference between major and minor calyx.
Minor calyx is found to be present in the liver.
Reabsorption of the useful products takes place in the distal convoluted tubule part of the renal tubule in the human body.
Where are the proximal and distal convoluted tubules located within the human body?
Cortical nephrons are found in the renal medulla.
Blood vessel draining the glomerulus in a mammalian nephron is called:
Urine is collected in the urethra.
