Muscular System of Humans
Muscular System of Humans: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Muscle Bundles, Muscle Fibre, Myofibril, Sarcomere, Contractile Proteins, Myoglobin, Red Muscle Fibres, Cori Cycle, Phosphocreatine/Creatine phosphate, Muscular System in Human, Skeletal Muscle, Myosin, etc.
Important Questions on Muscular System of Humans
The certain drug acts at synapses and affects the action of neurotransmitter substances. The effects of four different drugs are given below:
Drug-I: Inhibits the enzyme cholinesterase.
Drug-II: Prevents the release of acetylcholine.
Drug-III: Competes with acetylcholine at receptor sites.
Drug-IV: Inhibits the enzyme which destroys nor-adrenaline.
Which two drugs would prevent a skeletal muscle from responding to an electrical stimulus of the presynaptic neuron?
Myoglobin helps in the transport of oxygen in _______.
All or none law is not applicable for
In muscle contraction, this ion is essential:
Which one of the following proteins does not play a role in skeletal muscle contraction?
When the muscle fibres get excited, triad allows releasing of which ions?
Fibrous membrane in the middle of a sarcomere is
Identify the correct order of stages in muscle contraction
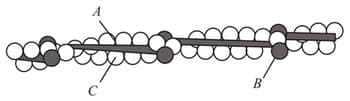
Identify the part labelled as in the above diagram of thin filament of a myofibril.
Following statement holds true for "Cori cycle"
A - band in skeletal muscle doesn't contain:
Fibrous membrane in the middle of sarcomere is
Strongest muscles in human body are found in
Which yield during muscle contraction?
Which of these statements about the molecular structure of myofilaments is true?
The long protein molecule, which masks the active sites on the actin is
Which statement is correct for muscle contraction?
When a skeletal muscle shortens during contraction, which of these statements is false?
During muscle contraction
Striated muscles contract because of
