Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Spermiation, Oogenesis, Oogonia, Primary Oocytes, Primary Follicle, Secondary Oocyte, Zona Pellucida, Ovulation, Progestogens, Structure of Sperm, Sperm Head, Middle Part of a Sperm, Tail of a Sperm, etc.
Important Questions on Gametogenesis
Where is acrosome present in human?
Mention four differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Assertion (A): In a woman after hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), the ovarian cycle is stopped.
Reason (R): Stoppage of FSH secretion.
The scar on the surface of an ovary is _____ (corpus luteum/corpus albicans).
Corpus albicans is a remnant of ovulation present on the surface of an ovary as a scar.
How does the formation of corpus albicans takes place in an ovary?
Corona radiata is the inner most layer of the granulosa cells and attached to the zona pellucida.
Write functions of the corona radiata in the egg.
What is the role of a primary follicle present in the ovary of a female?
What does the label 'A' indicate in the given picture? Name the cells present in this structure.
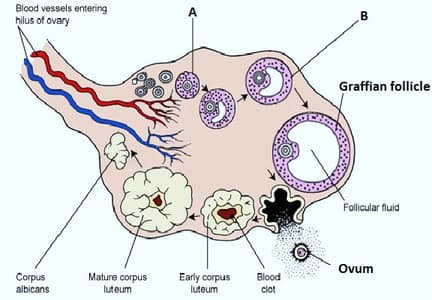
A stratified epithelium is formed from the cuboidal cells during the formation of primary follicles.
The flattened layer of follicular cells named primordial follicle turns cuboidal and proliferate to form _____ (membrane granulosa/zona pellucida).
Give a brief account of the formation of the granulosa cells.
Sperm has many mitochondria present in the tail and provide energy for its movement.
Draw and label the structure of a human sperm.
Where does spermatogonia present in the human body? What is its function?
Four polar bodies are formed during oogenesis.
Explain the formation of the polar bodies.
What is the role of polar bodies in reproduction?
The number of polar bodies formed during the process of oogenesis is _____.
