Kingdom Monera
Important Questions on Kingdom Monera
Consider the following statements and state true (T) and false (F):
(a) Bacteria cannot live in snow and deep oceans.
(b) Halophiles are found in marshy habitat and are nutritionally heterotrophs.
(c) Under unfavourable conditions bacteria produce several types of spores.
(d) Bacteria show autotrophic or heterotrophic nutrition.
Select the features true for Mycoplasma:
(a) Has double-stranded circular DNA.
(b) Cannot survive in the presence of oxygen.
Select the incorrectly matched pair:
How many statements are correct for the given organism in figure?
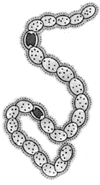
(i) Filamentous cyanobacteria as oxygenic photoautotroph.
(ii) Surrounded by mucilaginous sheath.
(iii) Heterocyst are specialized for N2 fixation.
(iv) Reproduce by hormogonia formation.
Consider the given figure and find out the correct option:
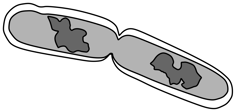
Bacterial endospores are
Archaebacterium shows similarity with Cyanobacteria in having
What is incorrect for Nostoc?
All the given characters are correct for Mycoplasma, except:
Clostridium botulinum is
Which of the following is incorrect w.r.t. Archaebacteria?
Read the following statements and select the correct options that are true for cyanobacteria:
(a) The colonies are generally surrounded by a gelatinous sheath.
(b) They form blooms in polluted water bodies.
(c) They show nitrogenase activity in heterocyst.
(d) They perform oxygenic photosynthesis in a vegetative cell only.
Match the column I and column II and select the correct option:
| Column -1 | Column - II |
| (a) Cholera | (ii) Clostridium |
| (b) Diphtheria | (ii) Salmonella |
| (c) Tetanus | (iii) Vibrio |
| (d) Typhoid | (iv) Corynebacterium |
**Two genera names were same, so one was changed.**
The Archaebacteria which occur in gut of ruminant animals
Out of the total, ___ (A)___ bacteria are photolithotrophic and they synthesize their food from ____(B)_____ substances.
The cyanobacteria have chlorophyll-a similar to green plants. These organisms
(a) are unicellular, colonial or filamentous, marine or terrestrial algae
(b) are surrounded by gelatinous sheath
(c) perform both carbon and nitrogen reduction
Bacteria reproduce mainly by
Which of the following bacteria are able to synthesize their food from inorganic raw material with the help of energy derived from oxidation of an inorganic substance?
Cyanobacteria are characterized by
Bacteria differ from Archaebacteria as the former

