Means of Transport in Plants
Means of Transport in Plants: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Porins,Diffusion,Uniport Diffusion etc.
Important Questions on Means of Transport in Plants
Movement and accumulation of ions across a membrane against their concentration gradient can be explained by:
Ringing/girdling experiments demonstrate
Consider the following statements:
A. Cytoplasmic streaming is passive process.
B. Aquaporins are present in some bacteria.
Which of them is/are correct?
When all the transporter proteins in a membrane are involved –
All the following affect the diffusion rates of substances in plants except:
Simple long distance transport cannot be achieved by
The path of movement of water is demonstrated by using
Unloading of mineral occurs at the fine vein endings through
Absorption of minerals by active transport is due to
Ions are absorbed from soil by
Minerals are mostly absorbed by
Which of the following moves by active transport?
(1) amino acid in proximal convoluted tubules.
(2) Absorption of most minerals by epidermal cells of root.
(3) pump
(4) Loading of sucrose from companion cell to sieve tube cells.
When molecules move across in a membrane independent of other molecule through carrier protein, then the process is known as
If two moves together in opposite direction and if two types of molecules move together in same direction, then such type of transport is known as
Choose the total number of correct statements from the following.
(1) Some channels in membrane are always open.
(2) Porins allow the passage of molecule of size up to small protein.
(3) Water channel is made up of eight different types of aquaporins.
(4) Facilitated diffusion is very specific.
Where porin proteins are present?
Identify A,B and C in the given figure.
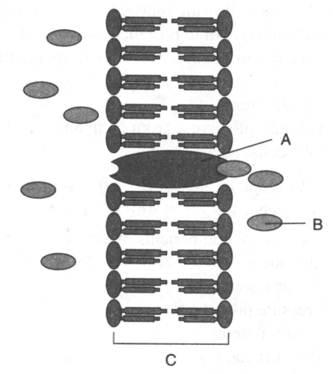
Facilitated diffusion requires _____ to transport substance across membrane.
Find out the total number of false statements from the following.
(1) The diffusion rate depends upon the size of substrate.
(2) Diffusion across membrane depends upon solubility of lipid.
(3) Membrane protein provides sites for hydrophilic substance to cross membrane.
(4) Facilitated diffusion does not require concentration gradient.
